Figure 1.
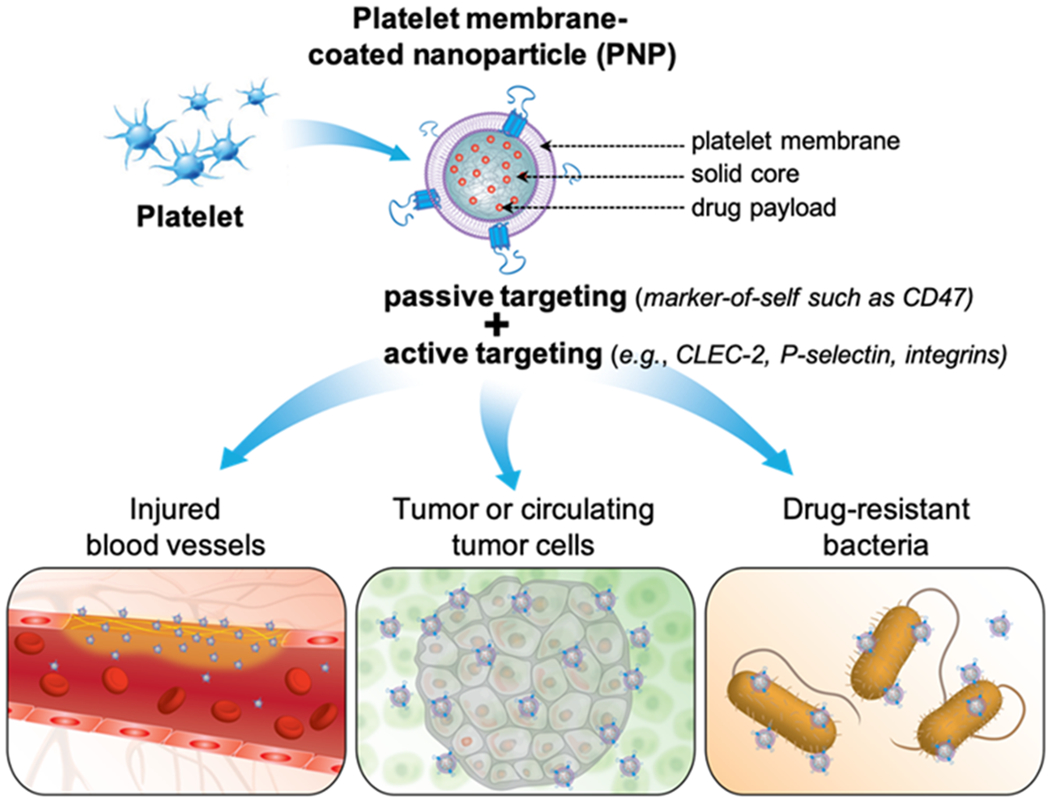
Schematic summary of using platelet membrane-coated nanoparticles (PNPs) for drug targeting. PNPs are made by wrapping membranes derived from natural platelets onto solid nanoparticle cores. PNPs leverage natural markers on the platelet membrane for drug targeting. The mechanism can be passive via markers-of-self such as CD47. It can also be active via surface antigens such as C-type lectin-like receptor 2 (CLEC-2), P-selectin, integrin α6β1, and integrin αIIbβ3. PNPs have been used to target drug payload to injured vasculatures (bottom left), tumor or circulating tumor cells (bottom middle), and drug-resistant bacteria (bottom right).
