Extended Data Figure 10. In vivo chemogenetics method, Split-TurboID, reveals a novel astrocytic cell adhesion molecule, NrCAM, that controls inhibitory synaptic organization.
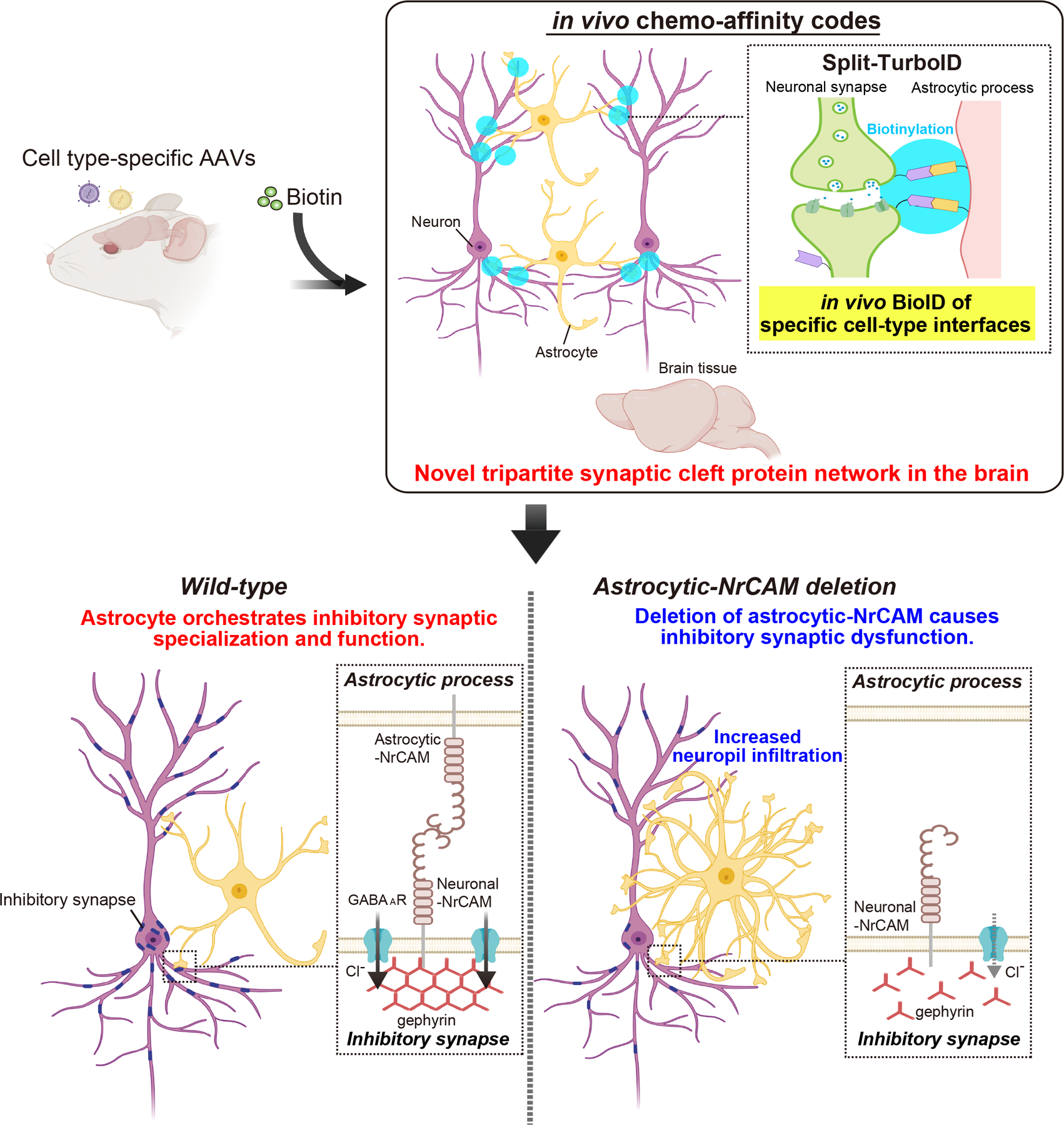
Development of in vivo chemo-affinity codes, Split-TurboID, and a working model of astrocytic NrCAM influencing inhibitory synaptic function. Split-TurboID can map the molecular composition of such intercellular contacts, even within the highly complex structure of the tripartite synapse in vivo. Mapping this interface, we discovered a new molecular mechanism by which astrocytes influence inhibitory synapses within the tripartite synaptic cleft via NrCAM. NrCAM is expressed in cortical astrocytes where it interacts with neuronal NrCAM that is coupled to gephyrin at inhibitory postsynapses. Loss of astrocytic NrCAM dramatically alters inhibitory synaptic organization and function in vivo.
