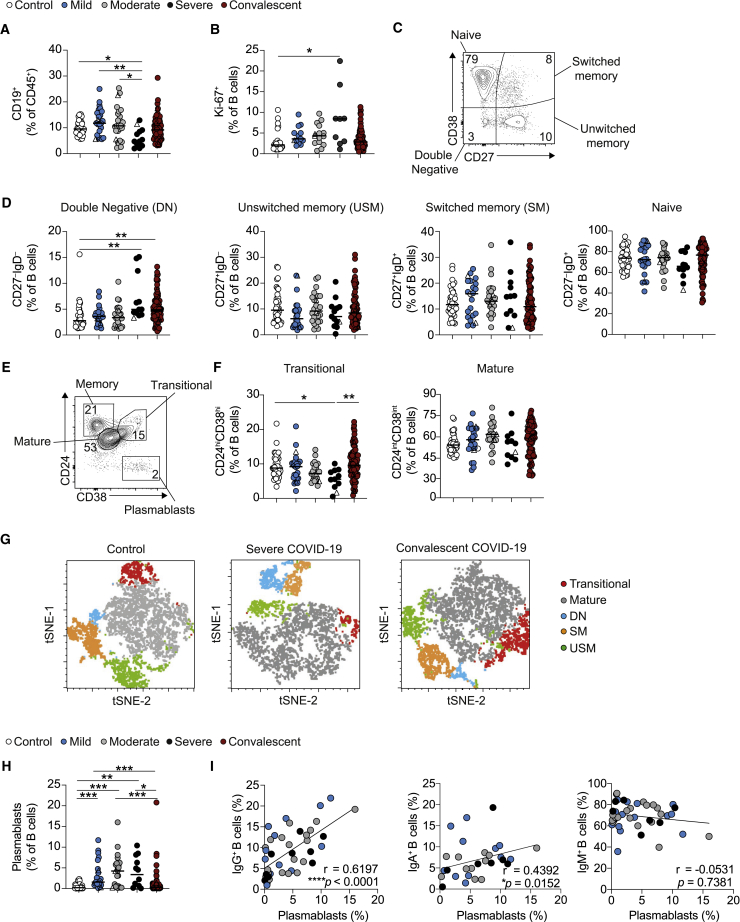
Figure 1.
Alterations in B cell subsets during acute COVID-19 are recovered upon convalescence
(A) Cumulative data show ex vivo frequency of CD19+ B cells in healthy individuals (n = 38) and COVID-19 patients with mild (n = 24), moderate (n = 26), and severe (n = 12) disease and at convalescence (n = 83).
(B) Cumulative data show Ki-67 expression by B cells in healthy individuals (n = 28) and COVID-19 patients with mild (n = 13), moderate (n = 15), and severe (n = 9) disease and at convalescence (n = 75).
(C and D) Representative flow cytometry plots and cumulative data show frequencies of naive (CD27−IgD+), unswitched memory (CD27+IgD+), switched memory (CD27+IgD−), and double-negative (CD27−IgD−) B cells in healthy individuals (n = 38–40) and COVID-19 with mild (n = 22–24), moderate (n = 25–26), and severe (n = 12–13) disease and at convalescence (n = 78–80).
(E and F) Representative flow cytometry plots and cumulative data show ex vivo frequency of CD24hiCD38hi transitional B cells and CD24intCD38int mature B cells in healthy individuals (n = 37) and COVID-19 patients with mild (n = 24), moderate (n = 23), and severe (n = 11) disease and at convalescence (n = 80).
(G) tSNE projection of flow cytometry panel visualizing B cell subsets in PBMCs. Representative images for healthy individuals, severe COVID-19 patients, and convalescent patients. Key indicates cell subsets identified on the image.
(H) Cumulative data show frequency of CD27hiCD38hi plasmablasts in healthy controls (n = 38) and COVID-19 patients with mild (n = 23), moderate (n = 23), and severe (n = 12) disease and at convalescence (n = 81).
(I) Graph showing correlation between plasmablasts and IgG+ (left), IgA+ (center), or IgM+ (right) B cell frequencies in acute COVID-19 patients. Graphs show individual patient data, with the bar representing median values.
In all graphs, open triangles represent SARS-CoV-2 PCR− patients. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, 1-way ANOVA with Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post hoc testing for multiple comparisons or Spearman ranked coefficient correlation test.
See also Figures S1 and S2.