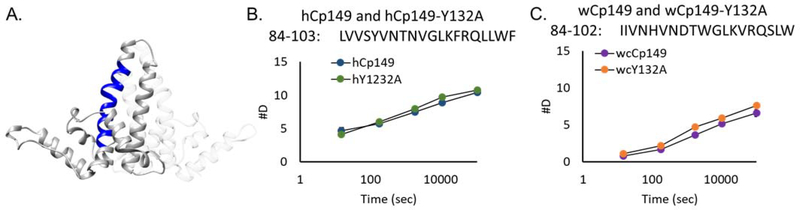
Figure 4.
Deuterium uptake in the intra-dimer interface. between hCp149 and wCp149 at the intra-dimer interface. Helix 4a which is comprised of amino acid residues 79–109, is central to stability at the intra-dimer interface (A). The peptide 84–103 in hCp149 or 84–102 in wCp149 is shown in blue. At the three-hour time point, the human peptide takes up 8.8 deuterium (B) whereas the woodchuck peptide takes up 5.1 deuterium (C). Even though the hCp149 peptide is longer by one amino acid residue, the difference is statistically significant with a p-value < 0.01 at all time points. Calculations of the intrinsic rate of exchange are within 5% for the two peptides.