Figure 1. Tunable HA-hydrogels as a supportive matrix to preserve LEC phenotypes.
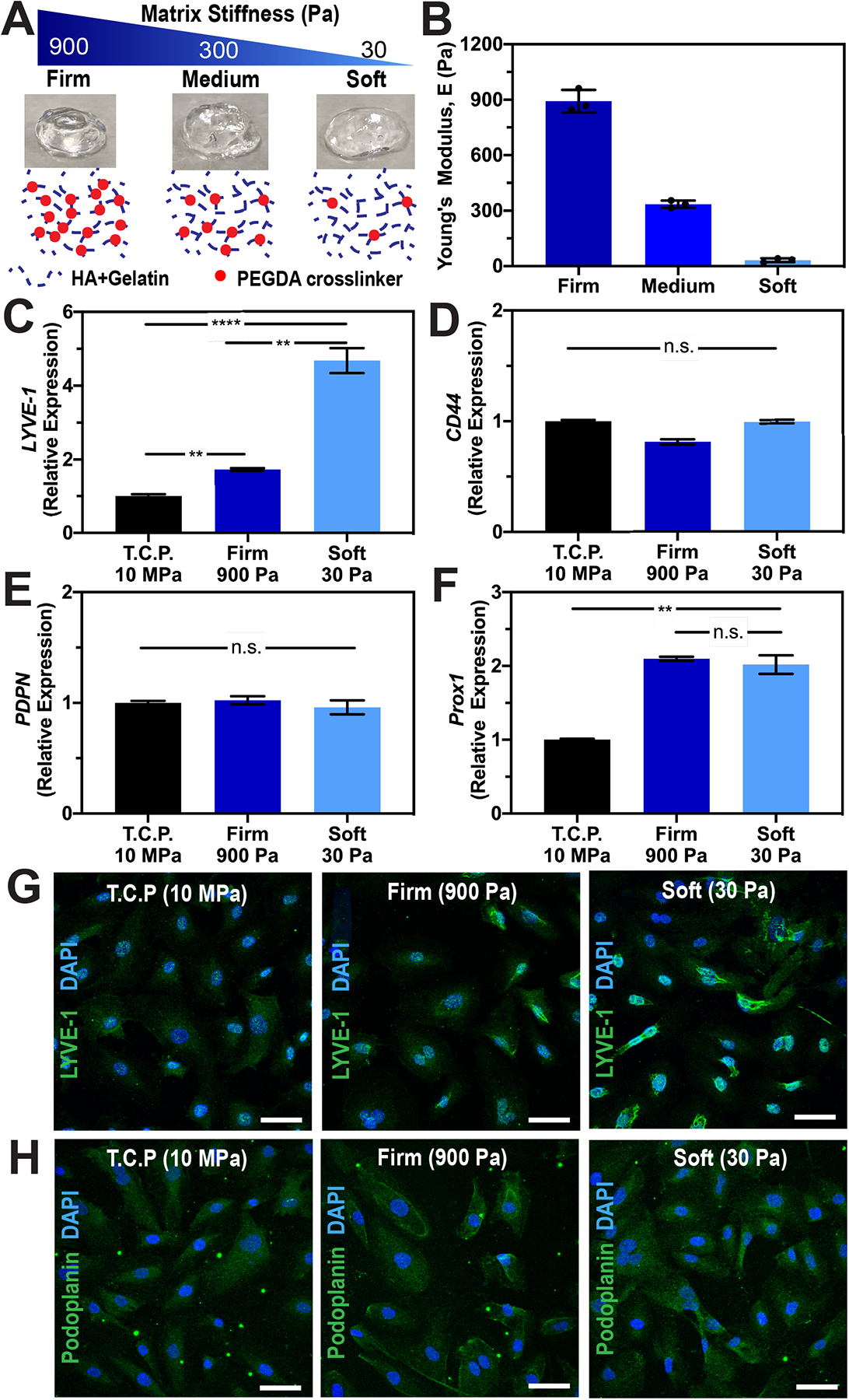
(A) Matrix elasticity of HA-hydrogels can be tuned with varying crosslinking density (red dots) without altering the polymer backbones (blue dotted lines). B) Rheological measurements of HA:gelatin in a 1:1 volume ratio with 2%, 1%, and 0.25% (w/v) of PEGDA crosslinker show three distinct profiles of hydrogel mechanics: firm, medium, and soft, respectively. Values shown are means ± S.D. of three independent hydrogel constructs. Please see Fig. S1 for storage (G’) and loss (G”) modulus data. Real-time qRT-PCR data for key lymphatic markers (C) LYVE-1, (D) CD44, (E) PDPN, and (F) PROX-1 expressed by LECs after being cultured on tissue culture plastic (E~10MPa), firm (E~900Pa), or soft (E~32Pa) HA-hydrogels. Three biological replicates (n=3) were collected per condition and analyzed with real-time qRT-PCR with triplicate readings. ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc analysis was performed to analyze differences between substrate stiffness. Significance levels were set at: n.s. P>0.05, * P<0.05, ** P<0.01 and *** P<0.001. Representative immunofluorescent images of LECs stained for (G) LYVE-1 and (H) Podoplanin after being cultured on tissue culture plastic (E~10MPa), firm (E~900Pa), or soft (E~32Pa) HA-hydrogels. Scale bars are 50 μm.
