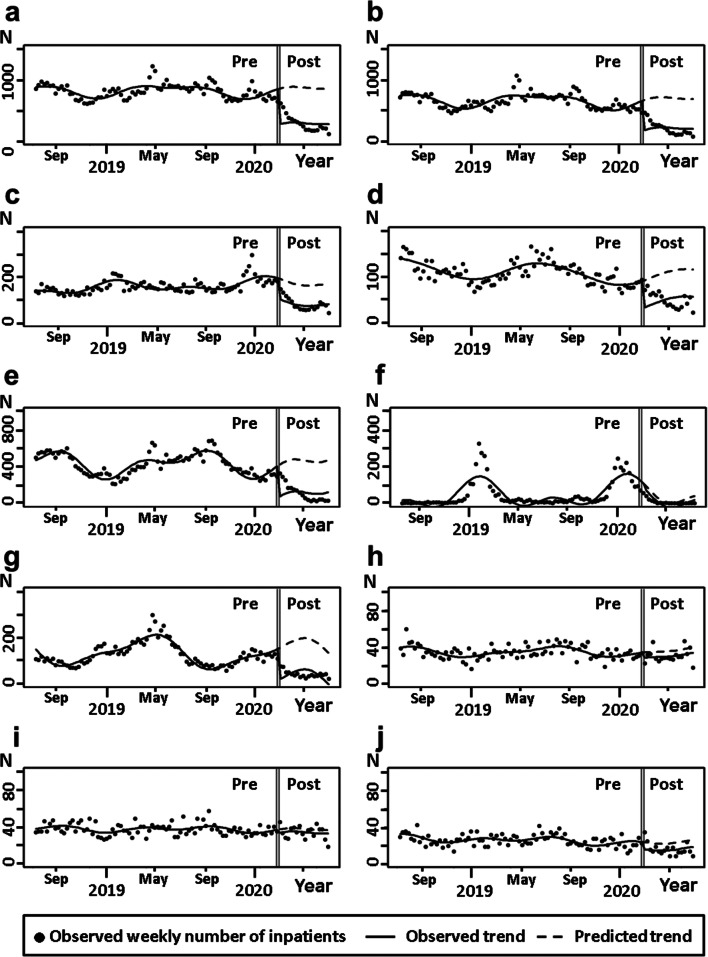
Fig. 2.
Time trend in the number of inpatients and the results of the interrupted time-series analysis. Black dots indicate the observed weekly number of inpatients, solid lines indicate observed trend following school closure for COVID-19, and dashed lines indicate predicted trend. Vertical double bars indicate the initiation of nationwide school closure in March 2020. The estimated coefficient (β) for the change in the number of inpatients per week, standard error (SE) for β and p value are as follows: a overall population (β = −581.1, SE 42.9, p < 0.001); b pre-school children (aged 0–5 years) (β = −491.9, SE 38.4, p < 0.001); c school-age children (aged 6–15 years) (β = −89.3, SE 9.0, p < 0.001); d patients with URTI (β = −59.2, SE 7.0, p < 0.001); e patients with LRTI (β = −347.5, SE 28.8, p < 0.001); f patients with influenza (β = −21.8, SE 16.5, p = 0.19); g patients with GII (β = −135.7, SE 9.2, p < 0.001); h patients with appendicitis (β = −5.7, SE 2.5, p = 0.027); i patients with UTI (β = −3.7, SE 2.4, p = 0.13); j patients with SSTI (β = −7.5, SE 2.3, p = 0.001). Abbreviations: COVID-19, coronavirus disease 2019; GII, gastrointestinal infection; LRTI, lower respiratory tract infection; SSTI, skin and soft tissue infection; URTI, upper respiratory infection; UTI urinary tract infection