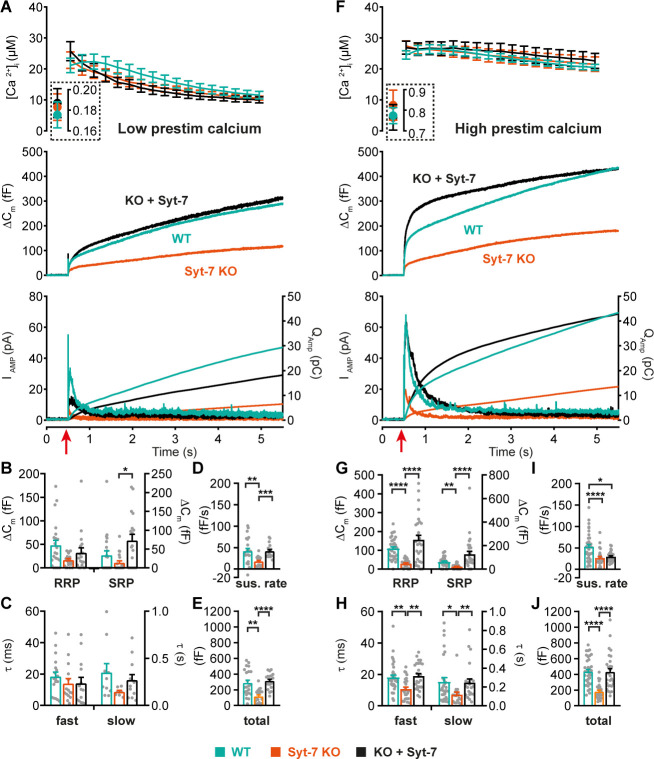
Figure 2. Syt-7 potentiates primed vesicle pool sizes at higher prestimulation [Ca2+].
(A) Calcium uncaging experiment from low prestimulation [Ca2+] in WT cells (persian green), Syt-7 KO cells (vermilion) and in Syt-7 KO cells overexpressing Syt-7 (black traces). Panels are arranged as in Figure 1A. (B) Sizes of the RRP and SRP. (C) Time constants of fusion for fast (i.e. RRP) and slow (i.e. SRP) secretion. (D) Sustained rates of secretion. (E) Total capacitance increase. (F) Calcium uncaging experiment from high prestimulation [Ca2+] in WT cells (green), Syt-7 KO cells (vermilion) and in Syt-7 KO cells overexpressing Syt-7 (black traces). Panels arranged as in Figure 1A. (G) Sizes of the RRP and SRP. (H) Time constants of fusion for fast (i.e. RRP) and slow (i.e. SRP) secretion. (I) Sustained rates of secretion. (J) Total capacitance increase. When stimulated from high prestimulation [Ca2+], Syt-7 expression potentiated RRP and SRP size. Data information: In (A–J) data with error bars are presented as mean ± SEM; in (A and F), the traces are the mean of all cells. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001. Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s post-hoc test. Number of cells in (A–E): Syt-7 WT: N = 22 cells; Syt-7 KO: N = 19 cells; Syt-7 KO + Syt-7: N = 18 cells, in (F–J) Syt-7 WT: N = 36 cells; Syt-7 KO: N = 27 cells; Syt-7 KO + Syt-7: N = 28 cells. Note that in cases where a cell did not have a given pool (SRP or RRP), the size of that pool was set to zero, and no time constant was estimated.
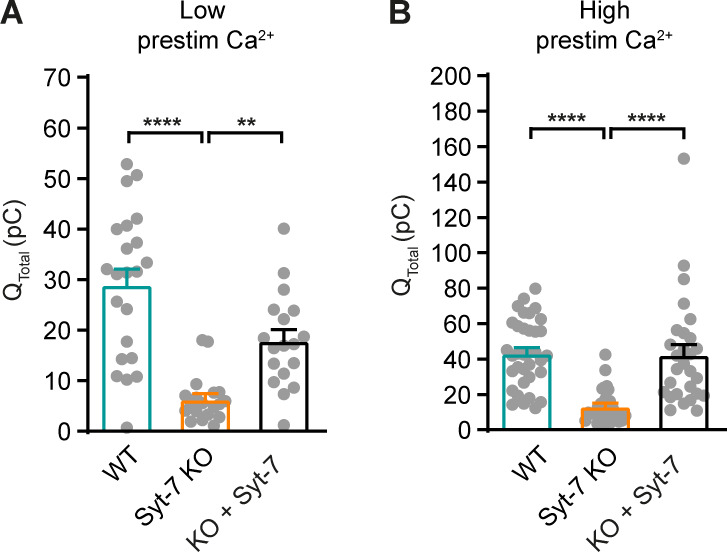
Figure 2—figure supplement 1. Amperometric charge quantification.