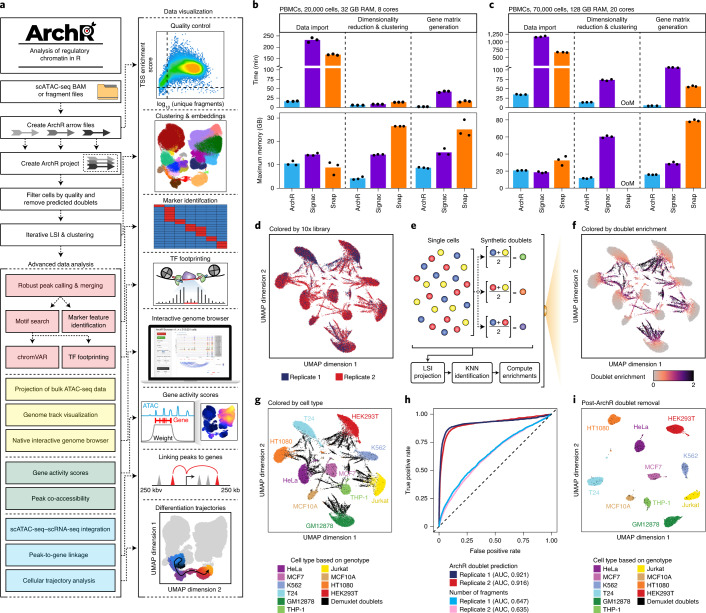
Fig. 1. ArchR, a rapid, extensible and comprehensive scATAC-seq analysis platform.
a, Schematic of the ArchR workflow from pre-aligned scATAC-seq data as BAM or fragment files to diverse data analysis. b,c, Comparison of runtime and memory usage by ArchR, Signac and SnapATAC (Snap) for the analysis of ~20,000 PBMCs using 32 GB of RAM and eight cores (b) or ~70,000 PBMCs using 128 GB of RAM and 20 cores (c). Dots represent replicates of benchmarking analysis (n = 3). OoM corresponds to out of memory. d, Initial UMAP embedding of scATAC-seq data from two replicates of the cell line-mixing experiment (n = 38,072 total cells from ten different cell lines), colored by replicate number. e, Schematic of doublet identification with ArchR. KNN, k-nearest neighbors. f,g, Initial UMAP embedding of scATAC-seq data from two replicates of the cell line-mixing experiment (n = 38,072 total cells from ten different cell lines), colored by the enrichment of projected synthetic doublets (f) or the demuxlet identification labels based on genotype identification using single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) within accessible chromatin sites (g). h, ROC curves of doublet prediction using ArchR doublet identification or the number of fragments per cell compared to demuxlet as a ground truth. The AUCs for these ROC curves are annotated below. i, UMAP after ArchR doublet removal of scATAC-seq data from two replicates of the cell line-mixing experiment (n = 27,220 doublet-filtered cells from ten different cell lines), colored by demuxlet identification labels based on genotype identification using SNPs within accessible chromatin sites.