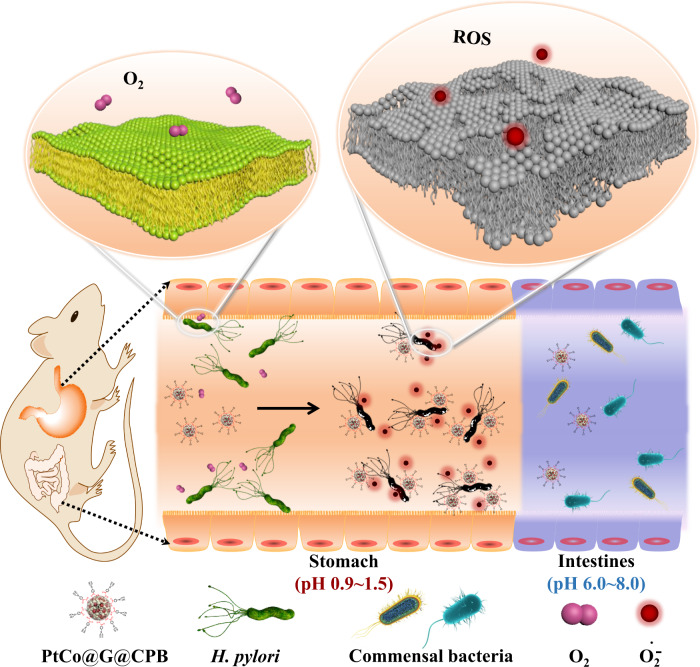
Fig. 3. The schematic of selective sterilization of H. pylori in vivo based on PtCo@G@CPB nanozyme.
In the acidic stomach condition, the PtCo@G@CPB nanozyme could specifically target H. pylori and catalyze ROS formation, showing significantly enhanced antibacterial efficacy. After entering neutral intestinal condition, the oxidase-like activity of PtCo@G@CPB would be suppressed, and it showed minimal toxicity towards commensal bacteria.