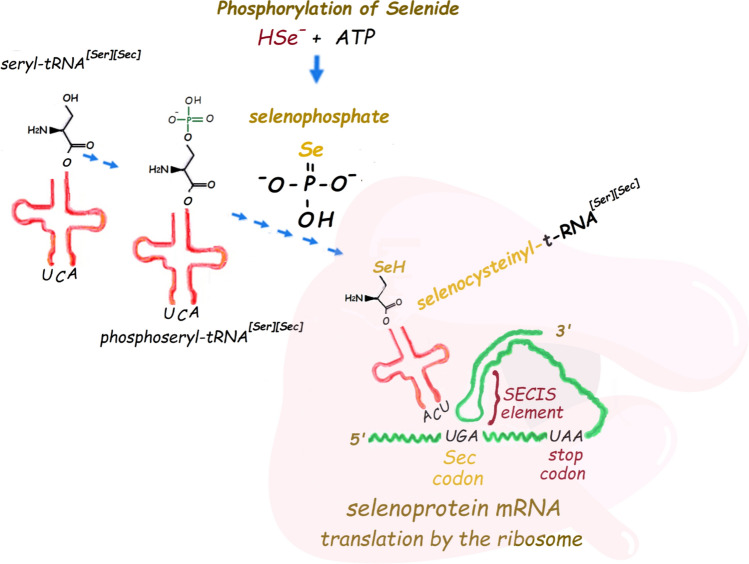
Fig. 2.
Incorporation of selenide in the phosphoseryl-t-RNA[Ser]Sec and synthesis of selenocysteinyl-t-RNA[Ser]Sec after the reaction of selenophosphate with the phosphorylated hydroxyl group of serine-loaded t-RNA[Ser]Sec. Selenocysteine is released from the t-RNA when the ribosome reads the UGA codon inside the mRNA sequence of a selenoprotein. The recoding of UGA codon to selenocysteine depends on the SECIS elements (which in mammals is a non-coding mRNA forming a stem-loop structure that kinks to interact with the t-RNA). The translation of the in-frame UGA codons inside the genes of selenoproteins also requires several protein factors that are not indicated in the figure (for more details, consult the text or the reviews Bulteau and Chavatte 2015; Howard and Copeland 2019; Simonović and Puppala 2018)