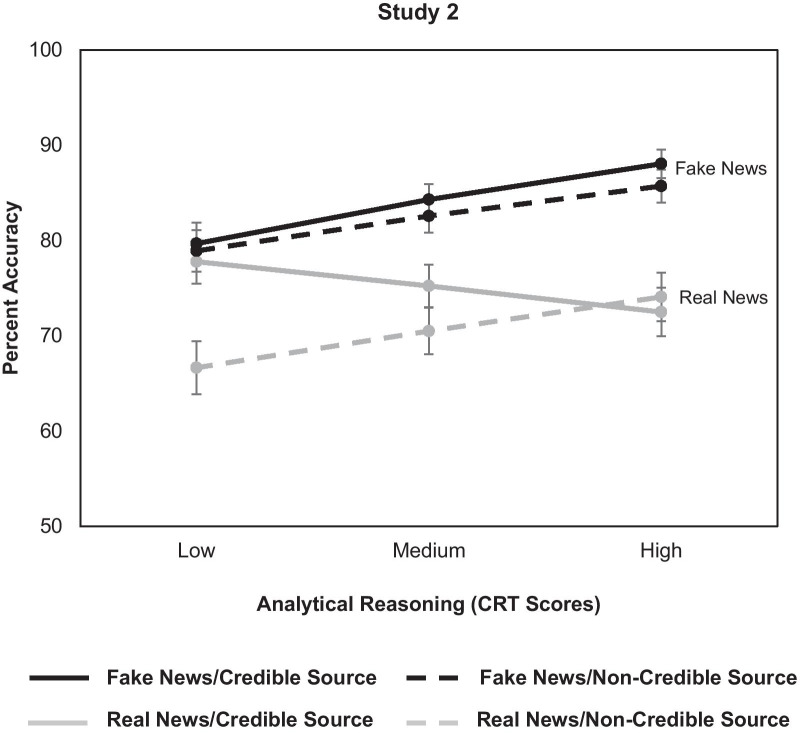
Fig. 2.
Veracity × CRT × Source interaction in Study 2; this 3-way interaction was not significant in Study 1. Percent accuracy for real (gray lines) and fake (black lines) news articles from credible (solid lines) and non-credible (dashed lines) news sources across levels of analytical reasoning (continuous; indexed by Cognitive Reflection Test (CRT) scores) in Study 2. Error bars denote standard errors. The medium analytical reasoning level indicates the mean CRT score in the current sample while the low and high levels indicate 1 SD below and above the mean CRT score, respectively. The y-axis start point reflects the 50% chance level. Lower analytical reasoning was associated with greater accuracy for real news paired with credible compared to non-credible sources, while news source did not influence accuracy for fake news across levels of analytical reasoning