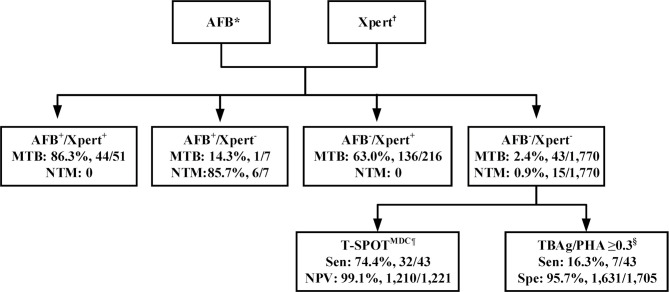
Figure 1.
Recommended algorithm for accurate and rapid diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in a real-world setting with high prevalence of M. tuberculosis and nontuberculous mycobacterium infections. *Three to four respiratory samples are recommended for AFB smear microscopy, with bronchoalveolar lavage liquid (BALF) preferred. †BALF preferred. ¶T-SPOTMDC (manufacturer-defined cutoff) has a supplementary role in ruling out pulmonary tuberculosis among AFB-/Xpert- patients. §TBAg/PHA (ratio of TBAg to PHA spot-forming cells, which is modified method calculating T-SPOT.TB assay results) ≥0.3 has a supplementary role in ruling in pulmonary tuberculosis among AFB-/Xpert- patients. AFB, acid-fast bacilli smear; AFB+, AFB smear positive; AFB-, AFB smear negative; Xpert, Xpert MTB/RIF; Xpert+, Xpert positive; Xpert-, Xpert negative; MTB, Mycobacterium tuberculosis; NTM, nontuberculous mycobacterium; T_SPOT, T-SPOT.TB; MDC, manufacturer-defined cutoff; TBAg, Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens; PHA, phytohaemagglutinin; Sen, sensitivity; PPV, positive predictive value; Spe, specificity.