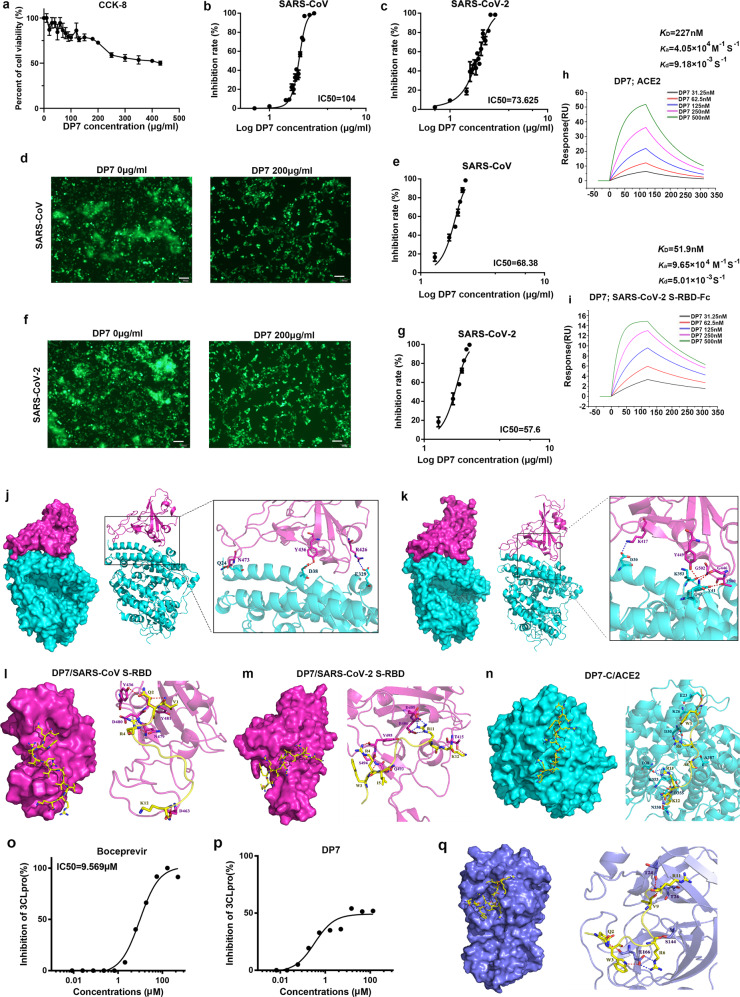
Fig. 1.
DP7 showed potent inhibitory activity against SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 infection. a Cytotoxicity test of DP7. DP7 inhibited the efficiency of (b) SARS-CoV S protein pseudovirus and (c) SARS-CoV-2 S protein pseudovirus infecting ACE2-293T. DP7 inhibited cell–cell fusion mediated by (d, e) SARS-CoV S protein and (f, g) SARS-CoV-2 S protein. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensorgram showing the binding kinetics for DP7 and (h) ACE2 and (i) S-RBD-Fc of SARS-CoV-2. Binding mode and interactions of ACE2 with (j) SARS-CoV S-RBD (PDB ID: 2AJF) and (k) SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD (PDB ID: 6LZG). Binding mode and interactions of DP7 with (l) SARS-CoV S-RBD, (m) SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD and (n) ACE2. Inhibitory activity of (o) boceprevir and (p) DP7 on SARS-CoV-2-3CLpro. q The surface binding model of SARS-CoV-2-3CLpro with DP7