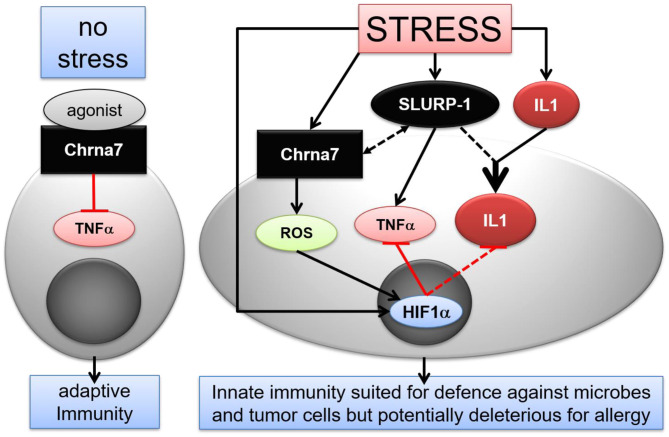
Figure 6.
Hypothetical scenario of stress interference with CS mediated immune modulatory effects in murine skin MC. Under normal conditions, activation of Chrna7 inhibits TNFα production by MC. In stress, however, SLURP-1 induces a shift in the immune response toward an innate pro-inflammatory state. SLURP-1 upregulates TNFα and IL1β expression by MC. Together with SLURP-1 and Chrna7, IL1β, and HIF1α are upregulated in MC by stress. Thereby, SLURP-1 promoted TNFα and IL1β production is inhibited by Chrna7 and ROS mediated HIF1α upregulation. However, SLURP-1 and IL1β synergize to produce an innate pro-inflammatory state. Thereby SLURP-1 may act as an allosteric ligand to Chrna7 and through Chrna7-unrelated, yet to be identified receptors (45, 88). Chrna, alpha nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; HIF, hypoxia inducible factor; IL, interleukin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SLURP, Secreted Ly-6/uPAR-related protein; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.