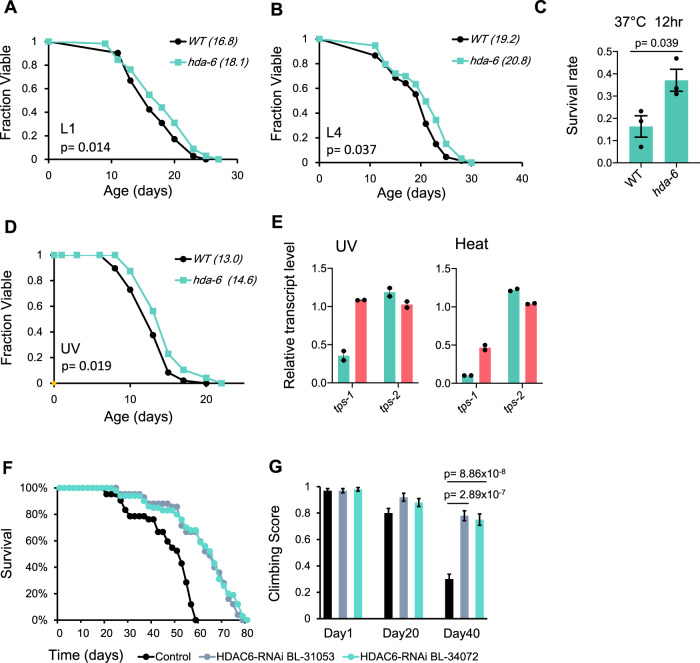
Fig. 6. Evolutionary conservation of HDA function.
A Lifespan of WT and hda-6 knockdown worms, RNAi treatment started at L1 stage, n = 176 for WT and 169 for hda-6. Statistical significance was calculated by two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. B Lifespan of WT and hda-6 knockdown worms, RNAi treatment started at L4 stage. n = 67 for WT and 93 for hda-6. Statistical significance was calculated by two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. C Survival rate of WT and hda-6 knockdown worms after 12 h incubation in 37 °C. Error bars represent SEM, three independent experiments were performed with 32 worms in each group. Statistical significance was calculated by two-sided t-test. D Lifespan of WT and hda-6 knockdown worms under 0.08 J/cm2 UV treatment. n = 50 for control and UV treatment group each. Statistical significance was calculated by two-sided Mann–Whitney U test. E RNA level of tps-1 and tps-2 genes in WT and hda-6 KO worms, under UV and heat. Two biological replicates were included in each group. F Lifespan analysis at 25 °C. N = 300 flies. Control group genotype: tub-Gal4, tub-Gal80ts / CyO; HDAC6 silencing group genotype: tub-Gal4, tub-Gal80ts/UAS-HDAC6-RNAi. Two independent HDAC6 RNAi lines (BL-31053 and BL-34072) were tested to avoid potential off-target effect. About 100 flies were tested for each group. G Climbing ability analysis at 5-, 20-, and 40-day-old adult flies. In all, 40 adult flies were tested in each age/genotype group. The results were presented as mean ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated by two-sided Mann–Whitney U test.