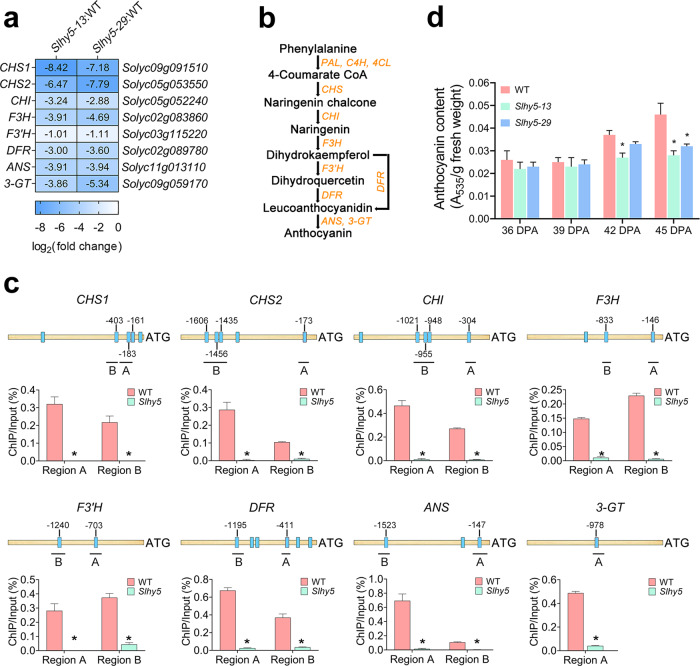
Fig. 4. Anthocyanin biosynthesis is regulated by SlHY5.
a Heatmap showing the differentially expressed genes involved in anthocyanin synthesis that were identified from the comparison of the Slhy5 mutant (lines Slhy5-13 and Slhy5-29) versus wild-type (WT) fruits at 39 days post anthesis (DPA) based on RNA-seq analysis. b Sketch diagram exhibiting the core anthocyanin biosynthesis pathway. c ChIP-qPCR assays showing that SlHY5 binds to the promoters of genes involved in anthocyanin synthesis. The promoter structures of the SlHY5 target genes are shown. The blue boxes represent ACGT-containing elements, and the numbers indicate the positions of these motifs relative to the translational start site. The black lines with uppercase letters represent the regions used for ChIP-qPCR. The values are the percentages of DNA fragments that coimmunoprecipitated with anti-SlHY5 antibodies relative to the input DNAs. ANS anthocyanidin synthase, CHI chalcone-flavonone isomerase, CHS1 chalcone synthase 1, CHS2 chalcone synthase 2, DFR dihydroflavonol-4-reductase, F3H flavanone 3-hydroxylase, F3′H flavonoid 3′-hydroxylase, 3-GT flavonol-3-glucosyltransferase. d Anthocyanin accumulation in Slhy5 mutants during fruit ripening. The error bars represent the standard deviations from three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate significant differences (*P < 0.05)