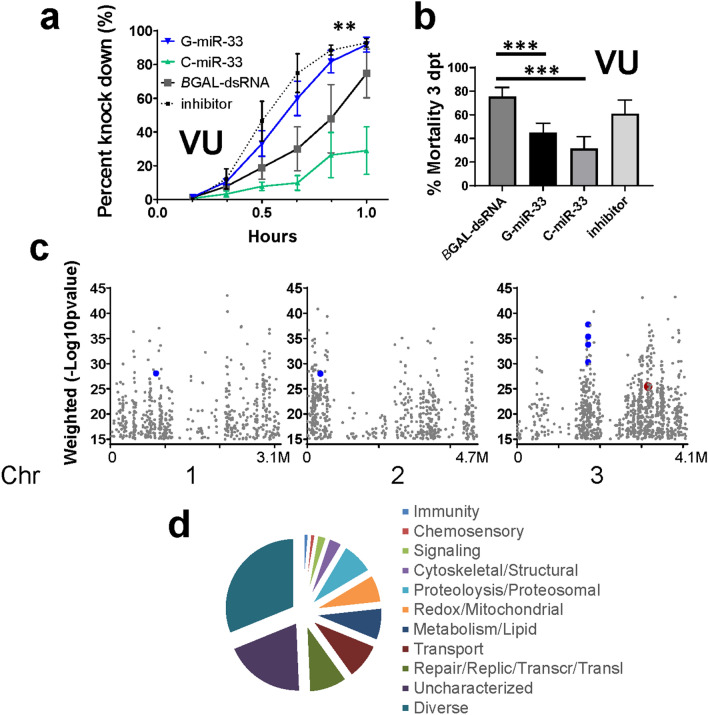
Figure 4.
VU permethrin toxicological response in the presence of excess miR-33 isoforms and VR vs VU strain genetic association data. (a) MiR-33 pre-miRNA over-expression affects permethrin toxicological response (knockdown) in VU. G-pre-miR-33 or C-pre-miR-33 were over-expressed in VU (Vergel-unselected) adult mosquitoes, or depleted with inhibitor, followed by standard bottle assays using a discriminating permethrin dose (1.5 µg per bottle) (ANOVA **p = 0.0042). (b) Mortality of individuals from treatment in (a) at 3 days post permethrin exposure (Fisher’s Exact test, G-***p = 0.0002 and C-***p = 1.0 × 10–5). (c) Genetic association analysis of target-capture gDNA deep sequencing shows genes arranged according to physical location along chromosomes. VGSC, − log10 (χ2 p value) 25.43 indicated in red, CYPs with scores higher than VGSC are highlighted in blue and enlarged for emphasis (Supplementary Table S3). (d) Two hundred ninety two genes with − log10 (χ2 p value) higher than VGSC were categorized according to predicted functional groups. Functional categories are indicated clockwise from top. Immunity 1.3%, Chemosensory 1.3%, Signaling 2.4%, Cytoskeletal/Structural 3.4%, Proteolysis/Proteosomal 7.9%, Redox/Mitochondrial 6.9%, Metabolism/Lipid 7.9%, Transport 8.9%, Repair/DNA Replication/Transcription/Translation (RRTT) 9.3%, Uncharacterized 19.5%, Diverse 31.1% (Prism GraphPad version 8.0., https://www.graphpad.com/scientific-software/prism/).