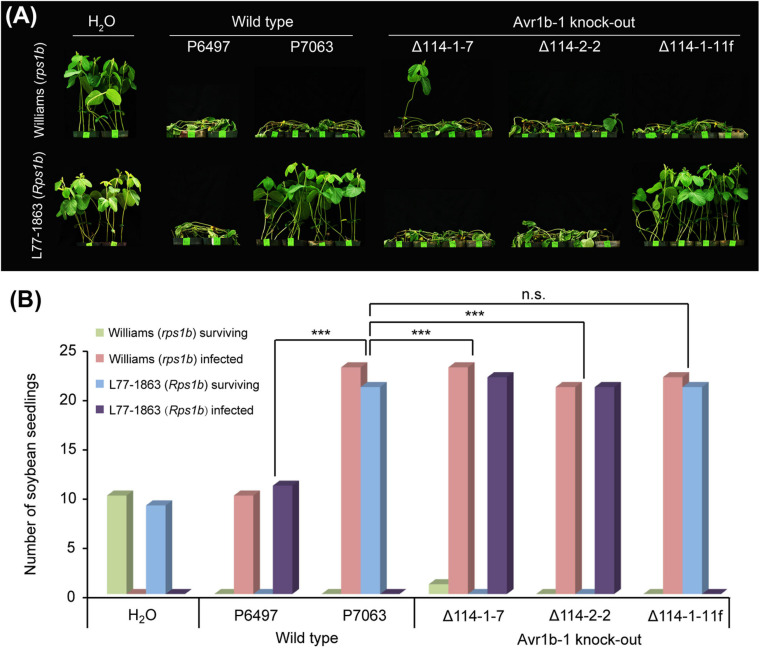
FIGURE 1.
Avirulence phenotypes of Avr1b-1 knock-out transformants measured by hypocotyl inoculations. (A) Avr1b-1-silenced wild-type isolate P6497, Avr1b-1-expressing wild-type isolate P7063, and two homozygous Avr1b-1 deletion transformants Δ114-1-7 and Δ114-2-2, plus a non-replacement transformant Δ114-1-11f were inoculated onto the hypocotyls of 7 day-old seedlings of soybean cultivar Williams (rps1b) or L77-1863 (Rps1b). Pictures were taken 3 days after wound inoculation. (B) Numbers of infected and surviving seedlings after inoculation with the P. sojae strains. A strain was deemed to be avirulent if the number of inoculated Rps1b seedlings surviving was significantly higher than the number of surviving seedlings without the Rps1b gene, and the number was not significantly different from the number of surviving seedlings inoculated with wild-type P7063. At least eight seedlings were used for the inoculation of each control or transformant. The significance of differences was determined by Fisher’s exact test (P < 0.001). *** = significant; n.s. = not significant.