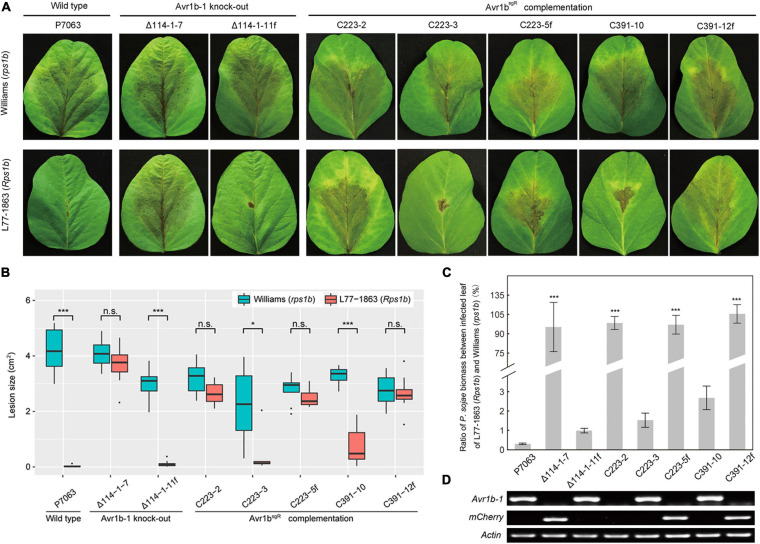
FIGURE 6.
Evaluation of avirulence activity of Avr1bsgR knock-in transformants. (A) Avr1bsgR knock-in transformants (C223-3 and C391-10) and control strains (wild-type P7063, Δ114-1-7, Δ114-1-11f, C223-5f, and C391-12f) were tested for avirulence by zoospore inoculation onto unifoliate leaves of Williams (rps1b) and L77-1863 (Rps1b). Pictures were taken 3 days after inoculation. (B) Average lesion sizes on the leaves of Williams (rps1b) and L77-1863 (Rps1b) measured on 10 unifoliate leaves from each of three independent experiments. Sizes were measured with ImageJ software. Error bars represent the mean ± standard deviation. P-values were calculated with Wilcoxon rank sum test, * and *** indicate P-value < 0.05 and < 0.001, respectively. (C) Avirulence phenotypes of Avr1b-1 knock-in transformants measured by real-time PCR-based quantification of P. sojae genomic DNA in infected tissue. Proliferation of P. sojae is plotted as the ratio between abundance of PsActin relative to GmActin DNA in infected L77-1863 leaves compared with Williams leaves at 72 hpi. This experiment was replicated three times. Error bars represent the mean ± standard deviation. P-values were determined by the Wilcoxon rank sum test. ***P < 0.001. (D) RT-PCR analysis of Avr1b-1 and mCherry transcripts in Avr1b-1 knock-in transformants. P. sojae Actin was used as the reference gene.