Fig 1.
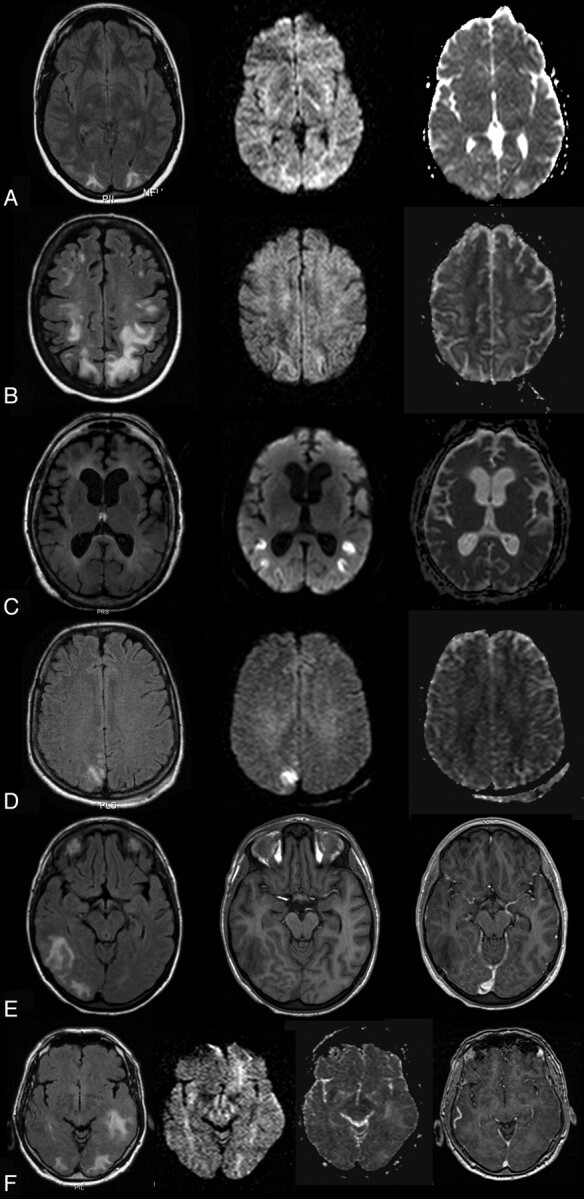
A, A 22-year-old woman with an albumin level of 24.7 mg/dL, on immunosuppressive medication (steroids and cyclosporine) and having systemic lupus erythematosus. Signal intensity is hyperintense bilaterally occipitally on FLAIR (left), isointense on DWI (middle), and hyperintense on ADC, indicating vasogenic edema. B, A 40-year-old woman with an albumin level of 21 mg/dL and blood pressure at the onset of 180/95 mm Hg and nephritis. Signal intensity is hyperintense bilaterally occipitally on FLAIR (left), isointense on DWI (middle), and hyperintense on ADC (right), indicating vasogenic edema. C, A 68-year-old woman with albumin levels of 38.3 mg/dL and chronic alcohol abuse. Her blood pressure at onset was 180/90 mm Hg. Signal intensity is isointense on FLAIR (left), hyperintense on DWI (middle), and hypointense on ADC (right), indicating cytotoxic edema. D, A 29-year-old woman with albumin levels of 37.8 mg/dL and eclampsia. Signal intensity is slightly hyperintense on FLAIR (left), hyperintense on DWI (middle), and isointense on ADC (right), indicating cytotoxic edema but also vasogenic components. E, A 19-year-old woman with an albumin level of 28.9 mg/dL, a hypertensive episode of 170/90 mm Hg, and renal failure. Signal intensity is hyperintense on FLAIR (left); there are no signal-intensity abnormalities on T1 (middle) and no gadolinium enhancement (left). F, A 78-year-old man with albumin levels of 22.6 mg/dL with immunosuppression (cyclosporine), renal transplantation, and blood pressure of 160/70 mm Hg. Signal intensity is hyperintense on FLAIR (left), isointense on DWI (middle left), hyperintense on ADC (middle right), and isointense on T1, indicating vasogenic edema.
