Figure 2.
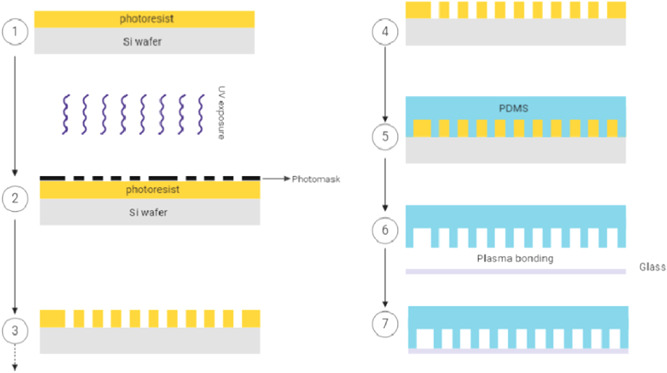
Schematic diagram of the SU‐8 soft‐lithography process for the manufacture of droplet‐based microfluidic devices. There are many methods of making microfluidic devices, but soft lithography is the most common process. In the soft lithography workflow, mold making, often created in SU‐8 negative photoresist, is needed for the replicating of PDMS microfluidic features. a small quantity of the SU‐8 was initially added to the silicon wafer (Si wafer) to produce the SU‐8 molds than to the spin‐coating according to the manufacturer's procedure. 1 The SU‐8 was pre‐baked. A mask with the desired design was used for fexposure of the spin‐coated wafer. SU‐8 photoresist undergoes a crosslinking reaction when exposed to UV light exposure. 2 , 3 A postexposure bake followed the exposure of the SU‐8 wafer. The next step was to eliminate the unexposed region with the developer. 4 Subsequently, the result is a micropatterned, formed mold. PDMS is poured over the SU‐8 master. 5 The molded PDMS is cured and bonded PDMS to glass by the plasma bonding technique. 6 , 7 ddPCR, droplet‐based digital PCR; PDMS, polydimethylsiloxane; UV, ultraviolet
