Figure 1.
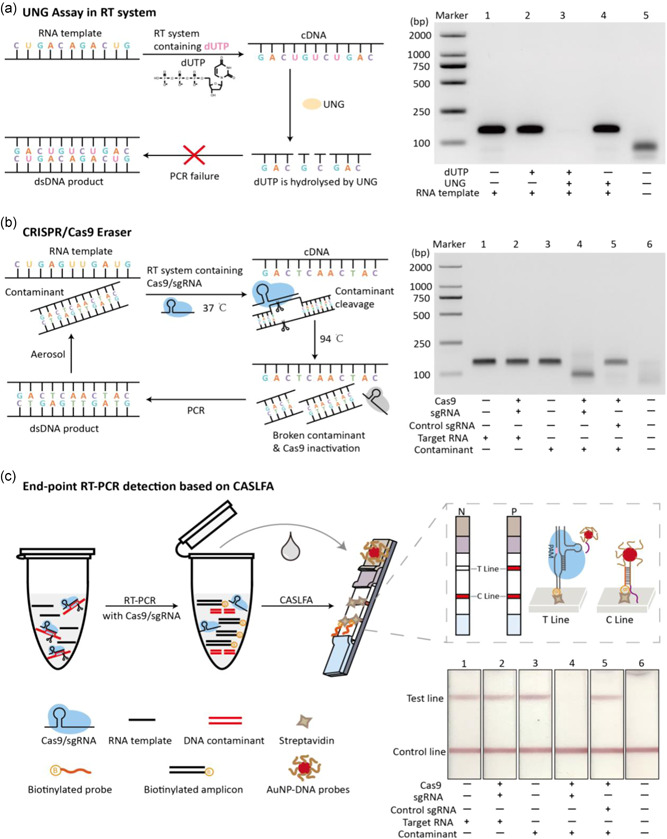
Development of CRISPR/Cas9 eraser for building contamination‐free RT‐PCR system. (a) UNG assay cannot be applied to one‐tube RT‐PCR system. Scheme presentation of UNG assay cannot be applied to RT‐PCR (left), and experimental confirmation of UNG assay cannot be applied to one‐step RT‐PCR (right). (b) Design of CRISPR/Cas9 eraser for RT‐PCR. Flow chart of CRISPR/Cas9 eraser working principle in RT‐PCR (left). Experimental confirmation of CRISPR/Cas9 eraser‐assisted contamination‐free RT‐PCR (right). (c) End‐point detection of RT‐PCR products by combining with CASLFA. The bottom right is the test strips analysis of the RT‐PCR products corresponding to (b). CASLFA, Cas9‐mediated lateral flow nucleic acids assay; cDNA, complementary DNA; CRISPR, clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat; RT‐PCR, reverse‐transcription polymerase chain reaction; sgRNA, single guide RNA; UNG, uracil‐N‐glycosylase [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
