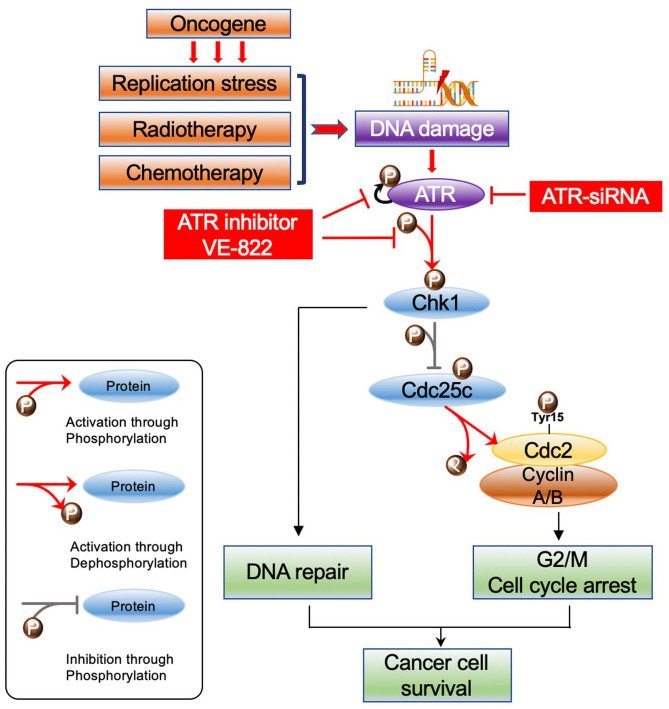
Figure 1.
Schematic of the ATR-Chk1 pathway. The oncogene promotes replication stress and DNA damage alongside radiotherapy and chemotherapy. In response, ATR kinase is preferentially activated. ATR then phosphorylates and hence activates Chk1. Chk1 then promotes DNA damage repair during G2/M cell cycle arrest. In brief, activated p-Chk1 phosphorylates and thus inactivates Cdc25c, which in turn inhibits the Cdc2-cyclin A/B complex through decreased dephosphorylation at Tyr15. This ultimately causes cell cycle arrest at G2. When ATR is knocked down or inhibited, p-Chk1 levels and downstream pCdc25c levels decrease. This increases the activity of the Cdc25c dephosphorylates pCdc2 (Tyr15), an inactive Cdc2 form, ultimately promoting mitosis.
ATR, ataxia-telangiectasia and Rad3 related; Chk1, checkpoint kinase 1.