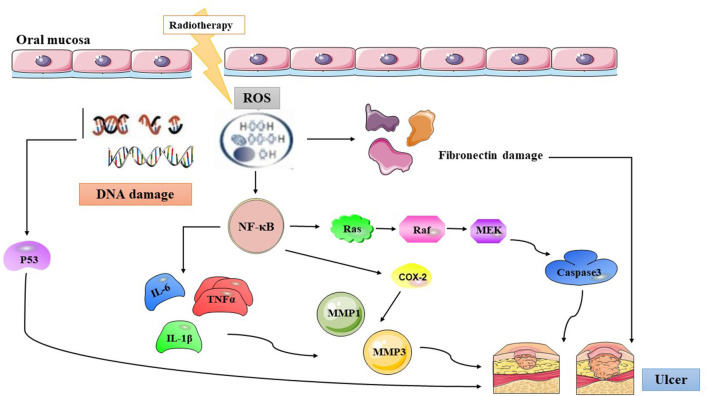
Figure 1.
The summary of radiation-induced oral mucositis pathogenesis. Radiotherapy results in direct and lethal DNA damage and releases reactive oxygen species (ROS) from epithelial and tissue macrophages in initiation phase. In primary damage phase, the DNA damage and ROS lead to three major steps: (1) fibronectin breakdown (2) P53 activation (3) nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation that stimulates to release pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as: TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, and IL-6. In the signal amplification phase, NF-κB stimulates the transcription of MAPK, COX-2, etc. The pathway of MAPK actives caspase3, and the other cytokines transmit signals that activate MMP1 and MMP3. Then the pseudomembrane or ulceration appear after around two weeks undergoing with symptomatic treatment of RIOM, and secondary infection adds more pro-inflammatory reactions. ROS, Reactive Oxygen Species; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa-B; IL-6, Interleukin-6; TNFα, Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha; IL-1β, Interleukin-1β; MMP 1, Matrix metalloproteinases 1; MMP 3, Matrix metalloproteinases 3; COX-2, Cyclooxegenase-2.