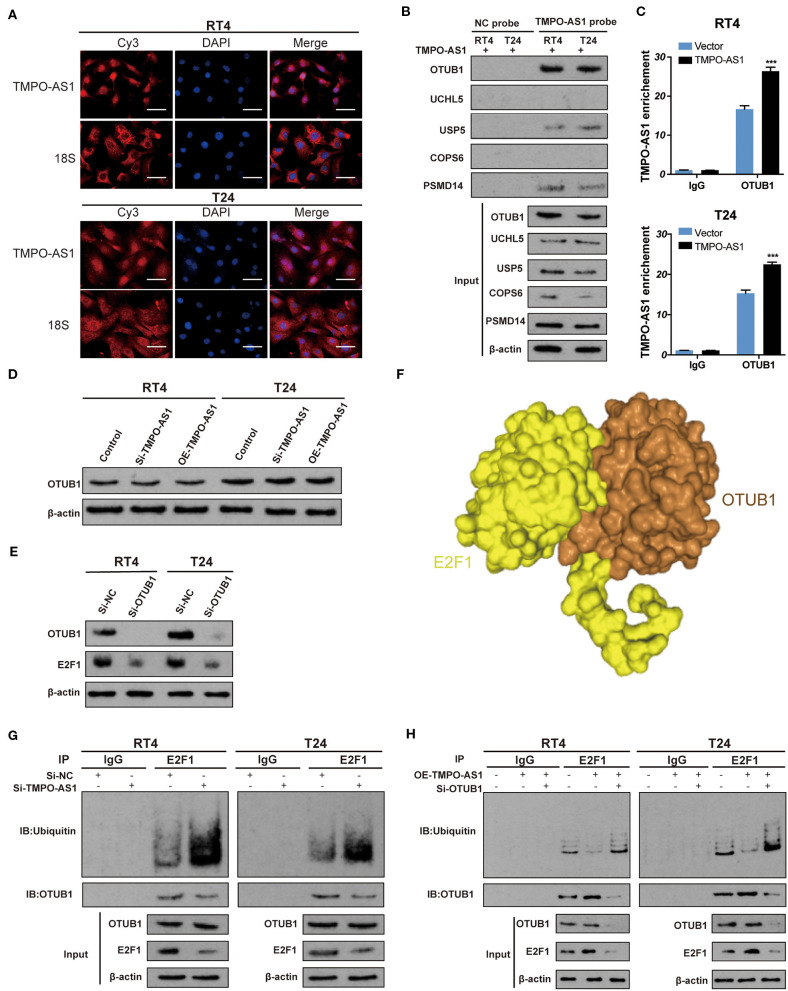
Figure 5.
TMPO-AS1 stabilizes E2F1 via OTUB1-mediated deubiquitination. (A) The TMPO-AS1 cellular localization was evaluated using FISH. (B) RNA pull-down assays demonstrated that OTUB1 is the deubiquitinase that most likely binds to TMPO-AS among a group of deubiquitinases (OTUB1, UCHL5, USP5, COPS6, and PSMD14). (C) RIP assays were performed to validate the interaction between TMPO-AS1 and OTUB1, in the context of TMPO-AS1 overexpressing RT4 and T24 cells; IgG was used as the negative control. Error bars represent the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. (D) Western blotting images show that TMPO-AS1 silencing has no effect on the OTUB1 protein levels in RT4 and T24 cells. (E) Western blotting images showing that the knockdown of OTUB1 leads to the decrease in the E2F1 protein levels in RT4 and T24 cells. Si- OTUB1, siRNA targeting OTUB1. (F) E2F1 (yellow) and OTUB1 (brown) are very likely to bind to each other as per HDOCK predictions. (G) Co-IP assays were performed in control or si-TMPO-AS1-treated RT4 and T24 cells using an anti-E2F1 antibody, followed by Western blotting to analyze the ubiquitin levels of E2F1. (H) RT4 and T24 cells transfected with the empty vector, and the construct for the overexpression of TMPO-AS1, alone, or together with si-OTUB1 were subjected to immunoprecipitation with an anti-E2F1 antibody, followed by Western blotting to analyze the ubiquitin levels of E2F1. ***p < 0.001.