Figure 2. Sealing of holes during biogenesis of double‐membrane organelles.
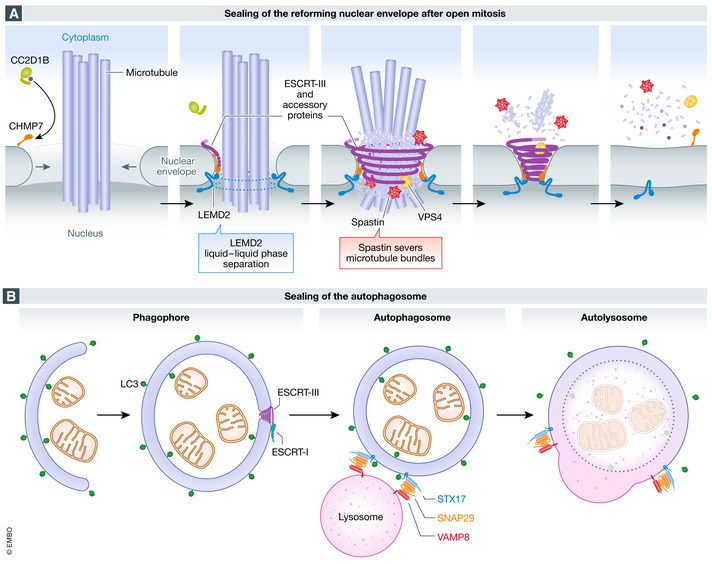
(A) sealing of the reforming nuclear envelope after open mitosis. During anaphase, when the reforming nuclear envelope meets microtubule bundles still connected to chromatin, the inner nuclear membrane protein LEMD2 undergoes liquid‐phase separation and activates the ESCRT‐III specific nuclear envelope recruitment factor CHMP7, which drives ESCRT‐III polymerization. Timing of ESCRT‐III recruitment is also regulated by CC2D1B, which prevents its premature localization to the reforming membrane. Spastin recruitment by ESCRT‐III is required for severing of mitotic spindle microtubules, while VPS4 modelling of ESCRT‐III filaments promotes membrane constriction and sealing. (B) sealing of the autophagosome. During autophagy, the double‐membrane phagophore expands to sequester cytoplasmic material for degradation. When the resulting LC3‐positive autophagosome is complete, a small hole remains. This hole is sealed by ESCRT‐III, which is recruited by ESCRT‐I. Sealing is followed by recruitment to the autophagosome membrane of the SNARE protein STX17, which forms a complex with the cytosolic SNARE SNAP29 and the lysosomal SNARE VAMP8, and this mediates fusion of the autophagosome with the lysosome to form an autolysosome.
