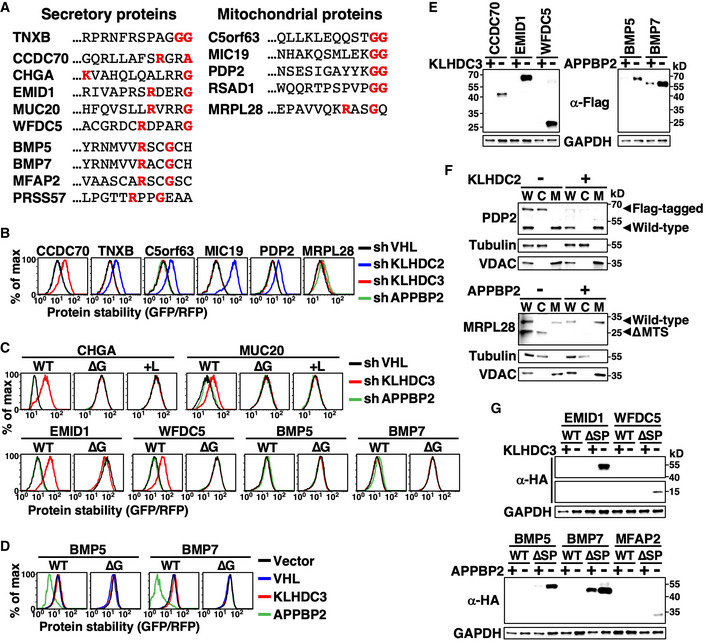
Figure 4. C‐degron pathways clear mislocalized cellular proteins.
-
AThe extreme C‐terminal sequence of indicated secretory and mitochondrial proteins. The diGly, R__G, and R_G_ motifs are labeled red.
-
BStability analysis of indicated proteins in cells treated with shRNAs against various BC‐box proteins. Since GFP was tagged at the protein N‐terminus and signal peptide and MTSs need to be exposed to be functional, all tested proteins were mislocalized.
-
C, DProtein stability analyses of wild‐type (WT) and mutant proteins lacking their extreme terminal Gly (∆G) or having it masked by adding Leu (+L) in cells with or without BC‐box protein knockdown (C) or overexpression (D).
-
EWestern blot analysis of Flag‐tagged proteins in cells with or without KLHDC3 or APPBP2 expression. The N‐terminal Flag abolished protein targeting. GAPDH serves as a loading control.
-
FFractionation and Western blot analysis of wild‐type and Flag‐tagged PDP2 (top), and wild‐type and MTS‐deleted (∆MTS) MRPL28 (bottom). Flag‐PDP2 and ∆MTS MRPL28 were mislocalized. W, C, and M denote whole cell lysates, cytosol fraction and mitochondrial fraction, respectively. Tubulin and VDAC serve as fractionation quality controls.
-
GProtein abundance analysis of HA‐tagged wild‐type or mutant secretory proteins with their signal peptide deleted (∆SP) in cells with or without KLHDC3 or APPBP2 expression. The HA epitope was inserted immediately after the signal peptide (SP), which had no impact on protein secretion.
Source data are available online for this figure.
