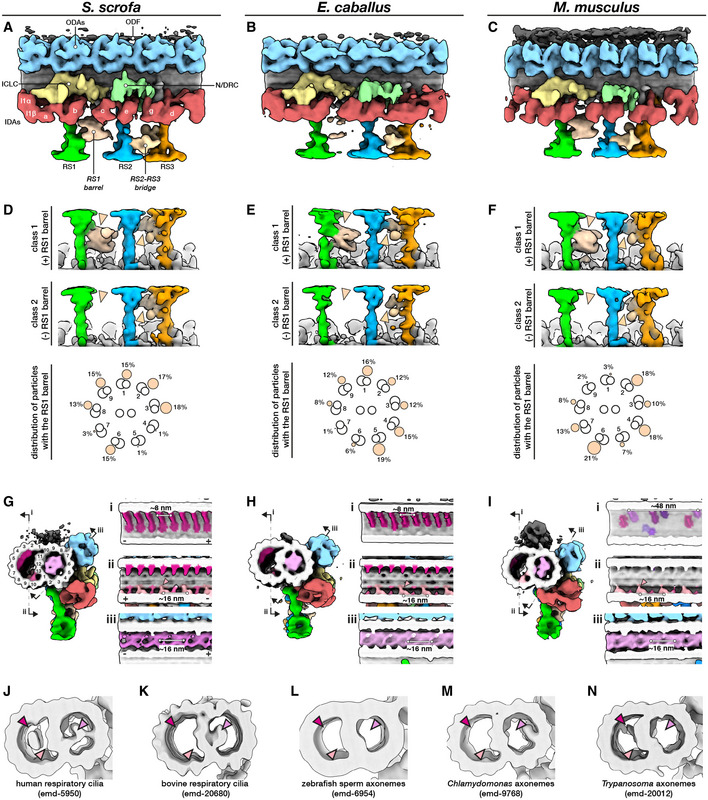
Figure 5. The mammalian sperm axoneme anchors unique accessory structures and species‐specific microtubule inner proteins.
-
A–CIn situ structures of the 96‐nm repeat from pig (A), horse (B), and mouse (C) sperm principal pieces.
-
D–FClassification focused on the RS1 barrel revealed two distinct classes of particles, one with (top panels) and one without (middle panels) the structure. Particles with the RS1 barrel are distributed asymmetrically around the axoneme (bottom panels).
-
G–IMicrotubule inner proteins in axonemes from pig (G), horse (H), and mouse (I) sperm.
-
J–NMicrotubule inner proteins in axonemes from other cell types and organisms. Arrowheads correspond to locations of MIPs that are prominent in mammalian sperm: magenta—helical MIP in the B‐tubule; pink—large A‐tubule MIP; light pink—additional density associated with MIP3a.
Data information: Labels: ODAs—outer dynein arms, IDAs—inner dynein arms, ICLC—intermediate chain/light chain of the I1 dynein, N/DRC—nexin/dynein regulatory complex, ODF—outer dense fiber, RS1‐3—radial spokes 1–3.
