Figure 9. Association between STING expression and clinical responses of human colon cancer patients, and a model of our findings.
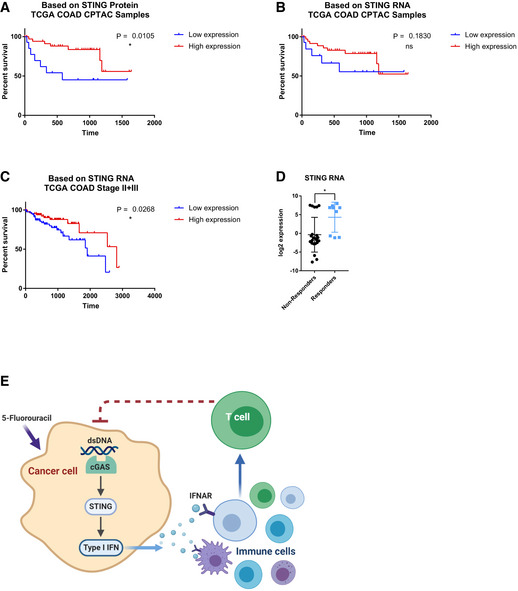
- STING protein expression of 58 colon adenocarcinoma specimens within the TCGA COAD collection were obtained from the CPTAC project website. Samples were partitioned into STING‐Low (non‐detectable STING protein, N = 15) and STING‐Hi (detectable STING protein, N = 43) groups. Kaplan–Meier curve is shown with P value indicated.
- STING RNA expression from the same 58 specimens were partitioned into STING‐Low (bottom 15 samples) and STING‐Hi (top 43 samples) groups. Kaplan–Meier curve is shown with P value indicated.
- Stage II and Stage III patients from the TCGA COAD dataset were partitioned into STING‐Hi (top 1/3 of samples, N = 87) and STING‐Low (bottom 1/3 of samples, N = 87). Kaplan–Meier curve is shown with P value indicated.
- From a published colorectal cancer chemotherapy response study, STING RNA expression in responders and non‐responders were compared, with each dot representing a tumor.
- A model summarizing our findings.
Data information: For panels (A–D), error bars represent SD, and center values represent mean. Log‐rank test was used to analyze survival data. Unpaired two‐tailed Student’s t‐test was used for comparing responders and non‐responders. *P < 0.05; ns: not significant.
