Figure 4.
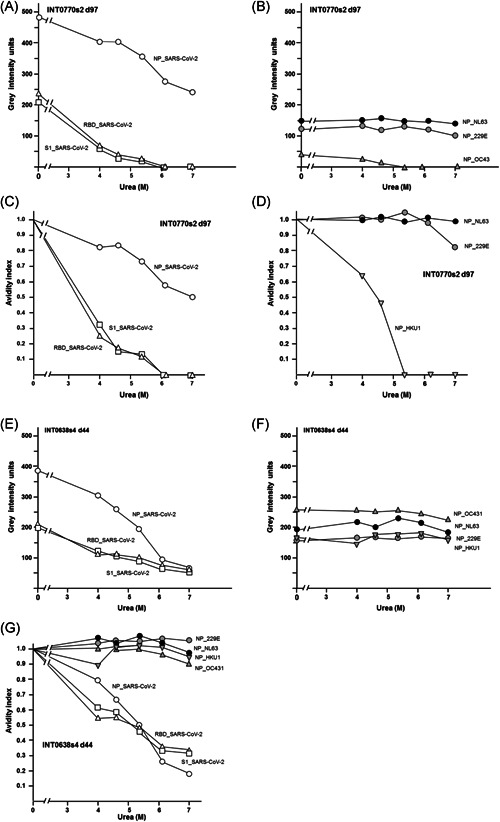
Comparison of gray intensity units and avidity indices obtained for IgG directed towards NP, RBD, and S1 of SARS‐CoV‐2 and NP of four seasonal coronaviruses. Sera taken from two COVID‐19 patients at (A–D) Day 97 or (E–G) Day 44 after onset of disease were tested in the recomLine SARS‐CoV‐2 assay, treated without urea or with increasing concentrations of urea, as indicated in the Figure. Gray intensity units (A, B, E, and F) and calculated avidity indices (C,D, and G) are presented. (A) The patient with the ID INT0770 shows a high gray intensity units for IgG towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 and a moderate reduction of gray intensity units after urea treatment, whereas gray intensity units for IgG towards RBD and S1 are lower, close together, and strongly reduced by urea treatment. (B) The patient also shows IgG towards NP of the seasonal coronaviruses NL63, 229 E, and OC43 in a much lower range of gray intensity units as measured for IgG towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 under A. The IgG towards NP of NL63 and 229 E is not significantly affected by urea treatment, whereas the very low concentration of IgG towards NP of OC43 is completely removed by urea. The analysis of the avidity indices (C,D) shows borderline avidity for IgG towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 and very low avidity for IgG towards RBD and S1 of SARS‐CoV‐2, whereas the avidity indices for IgG towards NP of NL63 and 229 E are very high, and very low for IgG towards NP of OC43. These data show that the IgG response towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 cannot be explained by cross‐reaction caused by IgG towards seasonal coronaviruses, as the concentration of IgG towards NP is lower than that of IgG towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 and the avidity indices of IgG towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 and those of IgG towards NP of the seasonal coronaviruses are not matching. The data shown for a second patient (ID INT0638) under (E–G) confirm these conclusions, as the gray intensity values measured for NP towards (E) SARS‐CoV‐2 are much higher than those for four (F) seasonal coronaviruses, and IgG towards NP of SARS‐CoV‐2 shows low avidity, whereas (G) the IgG towards the NPs of all four seasonal coronaviruses is of very high avidity. COVID‐19, coronavirus disease 2019; IgG, immunoglobulin G; NP, nucleoprotein; RBD, receptor‐binding domain; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2
