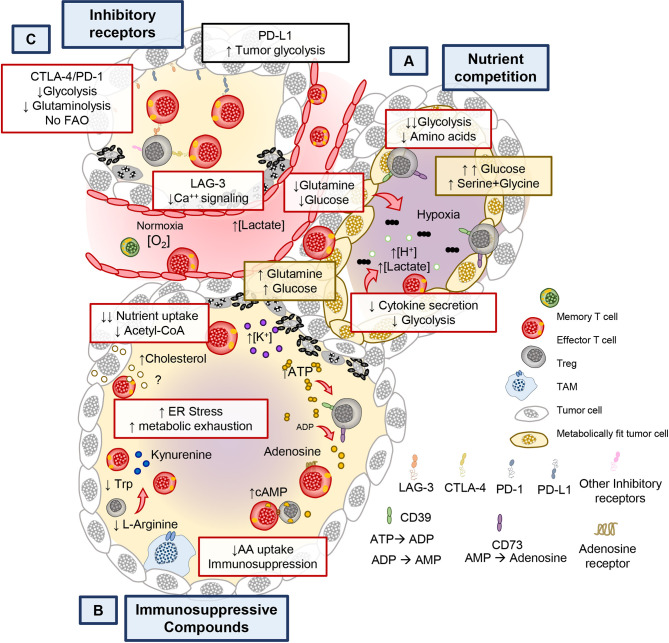
Figure 3.
Metabolic and immunological checkpoints that hinder T cell mediated tumor immunity. (A) Tumors can adapt their metabolism in response to nutritional stress to better compete and scavenge for glucose and amino acids to suppress T cell bioenergetics. (B) Chronic stimulation in the tumor bed leads to the expression of immune checkpoint receptors such as PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4, LAG-3, and they exert negative metabolic functions in T cells. (C) Furthermore, Ionic imbalances, oxygen availability, and metabolites impact the function of T cells. By products of immunosuppressive immune cells, cell debris and tumor metabolites create the conditions that contribute to the metabolic exhaustion of tumor specific T cells.