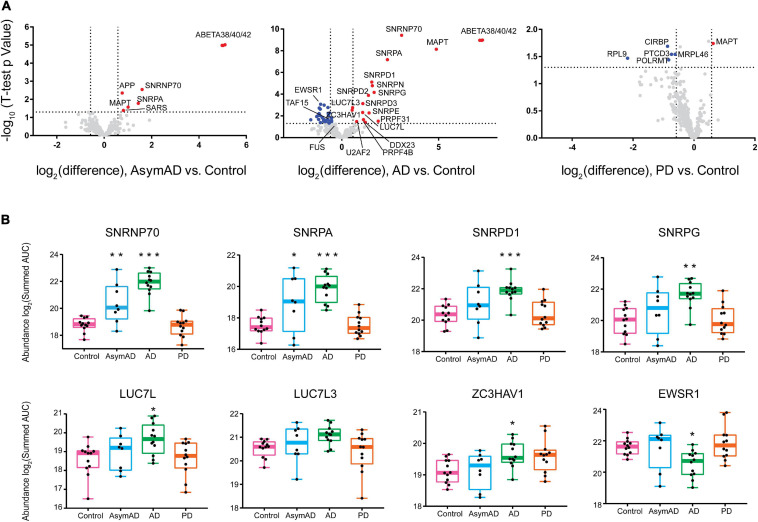
FIGURE 3.
RNA-binding proteins have different abundance patterns in the detergent-insoluble fractions across neurodegenerative diseases. (A) Differential abundance of RBPs across different groups was shown by volcano plot containing 385 RBPs, plus tau, APP and total β-amyloid. Fold-change, displayed on the x-axis, was the log2 protein abundance ratios for pairwise comparisons (AsymAD/Control, AD/Control, PD/Control). The t-statistic (−log10(p-Value)) was calculated for all proteins in each pairwise group and displayed on the y-axis. Insoluble fraction enriched proteins were highlighted in red (| Fold Change| > 1.5, p-Value < 0.05) while proteins with decreased insolubility were highlighted in blue, and gray dots represented proteins that remained unchanged. Several RBPs, including splicing factors, showed increased insolubility in AsymAD and AD while RBPs in PD were largely decreased in the insoluble fraction. (B) ANOVA boxplots of disease-signature RBPs (∗p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001). SNRNP70 and SNRPA showed stage-specific increase in detergent-insoluble fraction of AsymAD and AD; SNRPD1, SNRPG, LUC7L, and ZC3HAV1 only showed significant increase in AD insoluble fractions; FET family member EWSR1 exhibited a decreased abundance in AD insoluble fractions.