FIGURE 3.
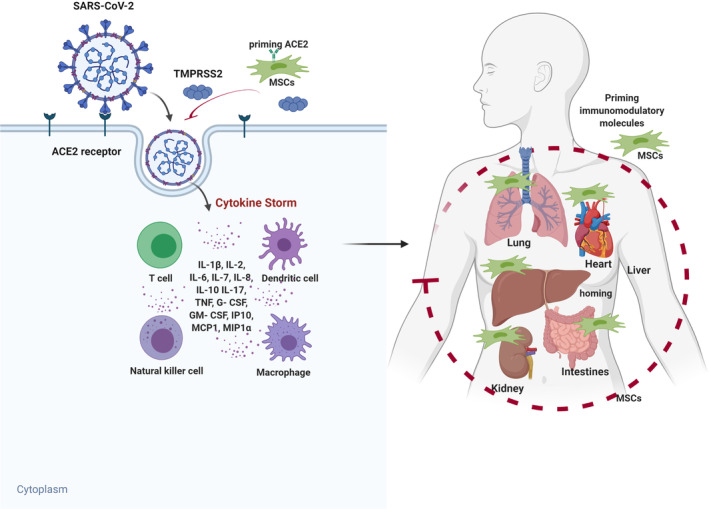
Potential mechanism of MSC action in COVID‐19 infected patients. SARS‐CoV‐2 enters cells through receptor‐mediated endocytosis via interactions with cell surface protein angiotensin‐converting enzyme II (ACE2) receptor with the assistance of TMPRSS2 protease, thus triggering a complex immune response involved in T cells, dendritic cells, NK cells, and macrophages. These cells release high amounts of cytokines and chemokines responsible for the cytokine storm, leading to symptoms and major organ dysfunction. Engineering MSCs with immunomodulatory molecules enhance the efficacy of homing to damaged tissues or cells and attenuate the cytokine storm, ultimately improving patients' outcome. Figure drawn with BioRender (https://biorender.com/). G‐CSF, granulocyte‐colony stimulating factor; GM‐CSF, granulocyte‐ macrophage colony‐stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; IP10, interferon gamma‐induced protein 10; MCP1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; MIP1α, macrophage inflammatory protein 1‐alpha.; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; NK, natural killer; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; TNF, tumor necrosis factor
