Figure 6.
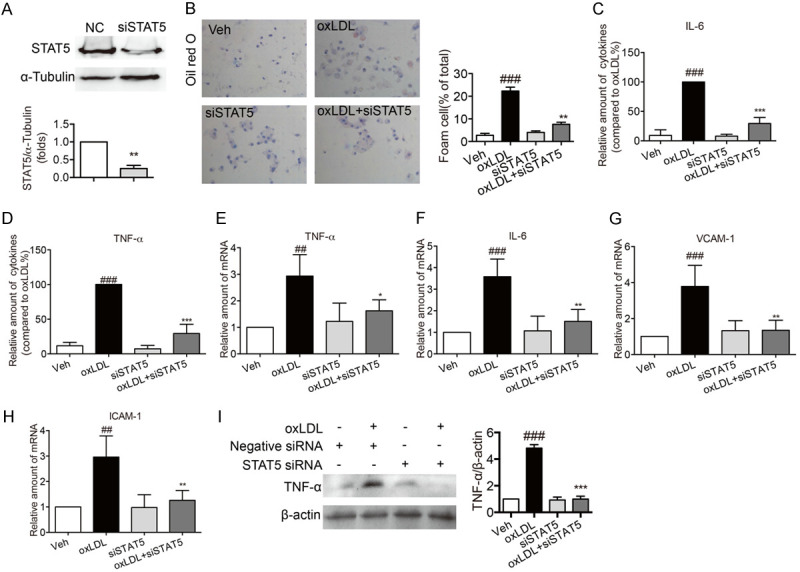
Knockdown of STAT5 by siRNA suppressed foam cell formatting and inflammation in oxLDL-stimulated macrophages. Primary macrophages were transfected with mouse specific STAT5 siRNA. (A) Western blotting for the expression of STAT5. (Bars represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments; **P < 0.01, vs. vehicle group). (B) Representative images of oil red O staining showed that STAT5 knockdown inhibited oxLDL-induced foam cell formatting. Macrophages were stimulated with oxLDL (100 µg/mL) for 24 h. The foam cell formatting was observed by oil red O staining. (C, D) STAT5 knockdown inhibited the decrease in the secretion levels of inflammatory factors in oxLDL-induced macrophages. oxLDL (50 µg/mL) stimulated macrophages for 24 h. ELISA was used to measure the levels of IL-6 (C) and TNF-α (D). (E-H) STAT5 knockdown reduced the mRNA levels of IL-6, TNF-α, VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 in oxLDL-induced macrophages. oxLDL (50 µg/mL) stimulated macrophages for 6 h. The mRNA levels of IL-6 (E), TNF-α (F), VCAM-1 (G) and ICAM-1 (H) were detected by RT-qPCR. (I) STAT5 knockdown inhibited the decrease in the protein expression of TNF-α in oxLDL-induced macrophages. oxLDL (50 µg/mL) stimulated macrophages for 24 h and then the total protein was collected. The expression of TNF-α was detected by western blot. (Bars represent the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments; ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001, vs. vehicle group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. oxLDL group).
