Figure 3.
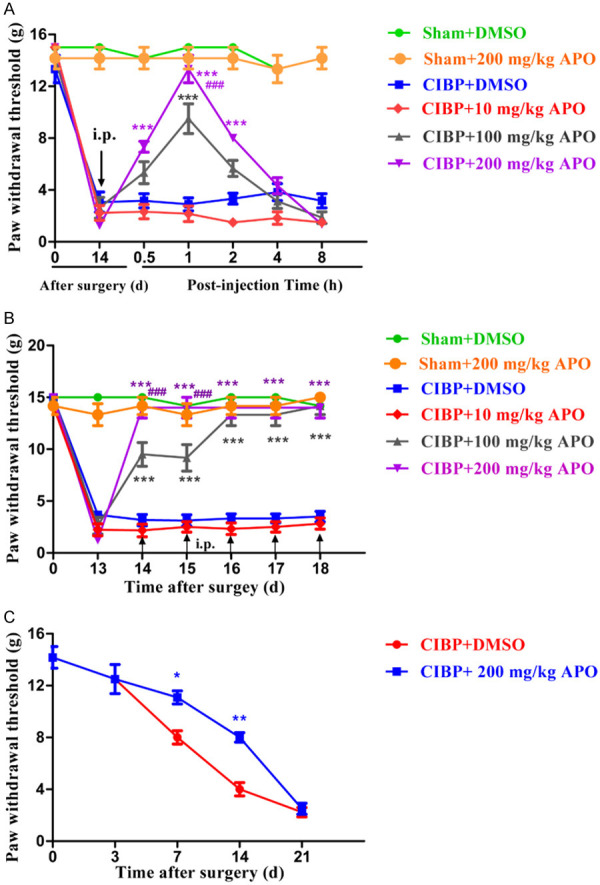
Analgesic effect of APO on established CIBP models. A. A single dose of APO (10, 100, 200 mg/kg, i.p.) was injected on day 14 after surgery. PWTs were performed at 0, 0.5, 1, 2, 4 and 8 h after injection of APO. Downregulation of PWTs was greatly inhibited by APO (100 and 200 mg/kg, i.p.) in CIBP rats. Upregulation of PWT began at 0.5 h, peaked at 1 h and lasted for 8 h. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with the CIBP + 200 mg/kg APO group, ###P < 0.001 compared with the CIBP + 100 mg/kg APO group, n= 6 in each group). However, 10 mg/kg APO had no significant effect on the PWTs compared with CIBP + 200 mg/kg APO group (P > 0.05). B. Chronic treatment with APO (200 mg/kg, i.p.) once daily for 5 consecutive days after surgery. PWTs were performed at day 13 and 1 h after APO injection each day. Repeated injection of APO (200 mg/kg, i.p.) markedly inhibited the mechanical allodynia in CIBP rats without tolerance (***P < 0.001 compared with the CIBP + DMSO group, ###P < 0.001 compared with the CIBP + 100 mg/kg APO group, n = 6 per group). C. Preventive effect of early treatment with APO on the development of CIBP. APO (i.p., 200 mg/kg once a day) or a mixture of DMSO, tween 80 and saline (2 ml, i.p.) was injected once daily from day 1 to day 5 after surgery. PWTs were performed before the test on day 3, 7, 14 and day 21. Treatment with 200 mg/kg APO showed significant downregulation in PWTs at day 7 and day 14 in CIBP rats compared with CIBP + DMSO group. However, PWTs showed no significant difference between these two groups at day 21. (*P < 0.5, **P < 0.001 compared with the CIBP + DMSO group. n = 6 per group).
