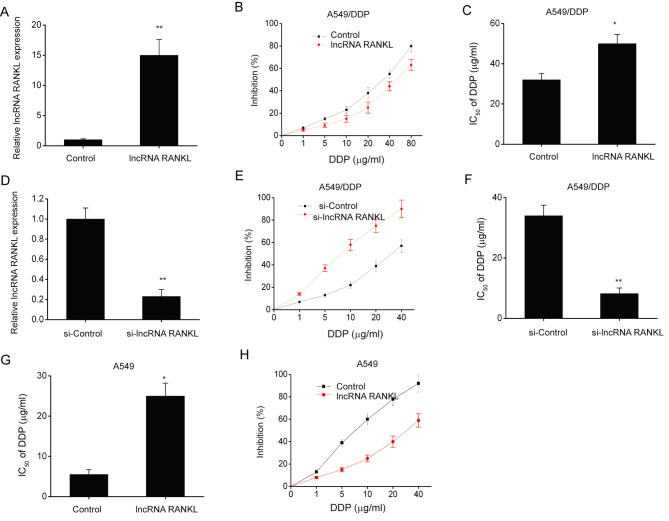
Figure 2.
RANKL contributes to DDP resistance in A549/DDP cells. (A) RANKL expression in A549/DPP cells that underwent stable transfection with RANKL lentiviruses was assessed using RT-qPCR. GAPDH was used as the internal control. (B) The effect of DDP on the inhibition rate of A549/DDP cells was evaluated via CCK-8 assay. (C) IC50 of DDP in A549/DPP cells was evaluated via CCK-8 assay. (D) Efficacy of siRNA in A549/DDP cells was assessed via RT-qPCR following 48 h transfection with si-Control or si-lncRNA RANKL. GAPDH was used as the internal control. (E) The effect of DDP on the inhibition rate of A549/DDP cells was evaluated via CCK-8 assay. (F) IC50 of DDP in A549/DDP cells was evaluated using the CCK-8 assay. (G) IC50 of DDP in A549 cells was evaluated using the CCK-8 assay. (H) The effect of DDP on the inhibition rate of A549 cells was evaluated using the CCK-8 assay. Data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05. **P<0.01. RANKL, receptor activator of nuclear factor-κ B ligand; DDP, cisplatin; RT-qPCR, reverse transcription-quantitative PCR; CCK-8, Cell Counting kit-8; IC50, half of the maximal inhibitory concentration; lncRNA, long non-coding RNA; si, short interfering.