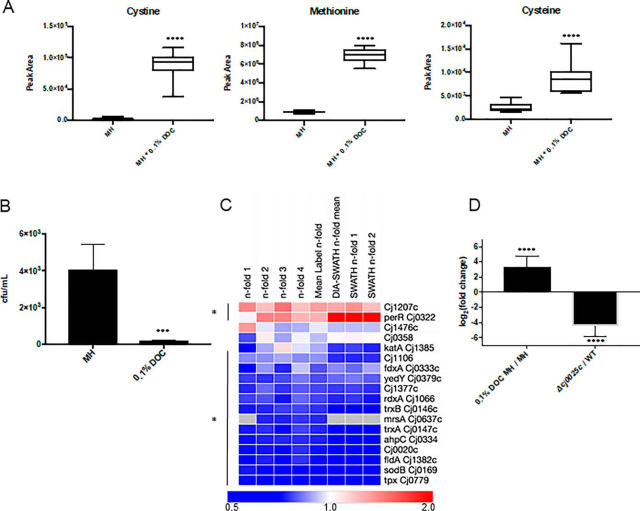
Fig. 4.
Increased intracellular sulfur-containing amino acids in C. jejuni NCTC11168 grown in DOC correlate with reduced resistance to oxidative stress and increased abundance of the Cj0025c putative sodium:dicarboxylate transporter.A, Comparative intracellular abundances of sulfur-containing amino acids in MH medium with or without 0.1% DOC measured by targeted LC-MS/MS metabolomics (**** p < 0.0001); B, Growth in 0.1% DOC reduces resistance against oxidative stress (cells were exposed to 5 mm H2O2 for 30 min, serial dilutions were plated onto MH agar for CFU enumeration; *** p < 0.001); C, Heat map of C. jejuni antioxidant proteins ordered by largest mean n-fold change (label-based discovery; top). Data from each of 4 label-based replicates (n-fold 1–4) and DIA-SWATH-MS validation (“DIA” mean of 2 biological replicates [DIA n-fold 1–2]) are shown. Values are gray where the protein was not identified in a biological replicate and/or by DIA-SWATH MS (* denotes proteins significantly altered in abundance); D, qPCR showing increased cj0025c gene expression in 0.1% DOC and removal of cj0025c expression in Δcj0025c C. jejuni.