Figure 1. Single-Cell RNA-Seq Profiling of the Developing Human Retina.
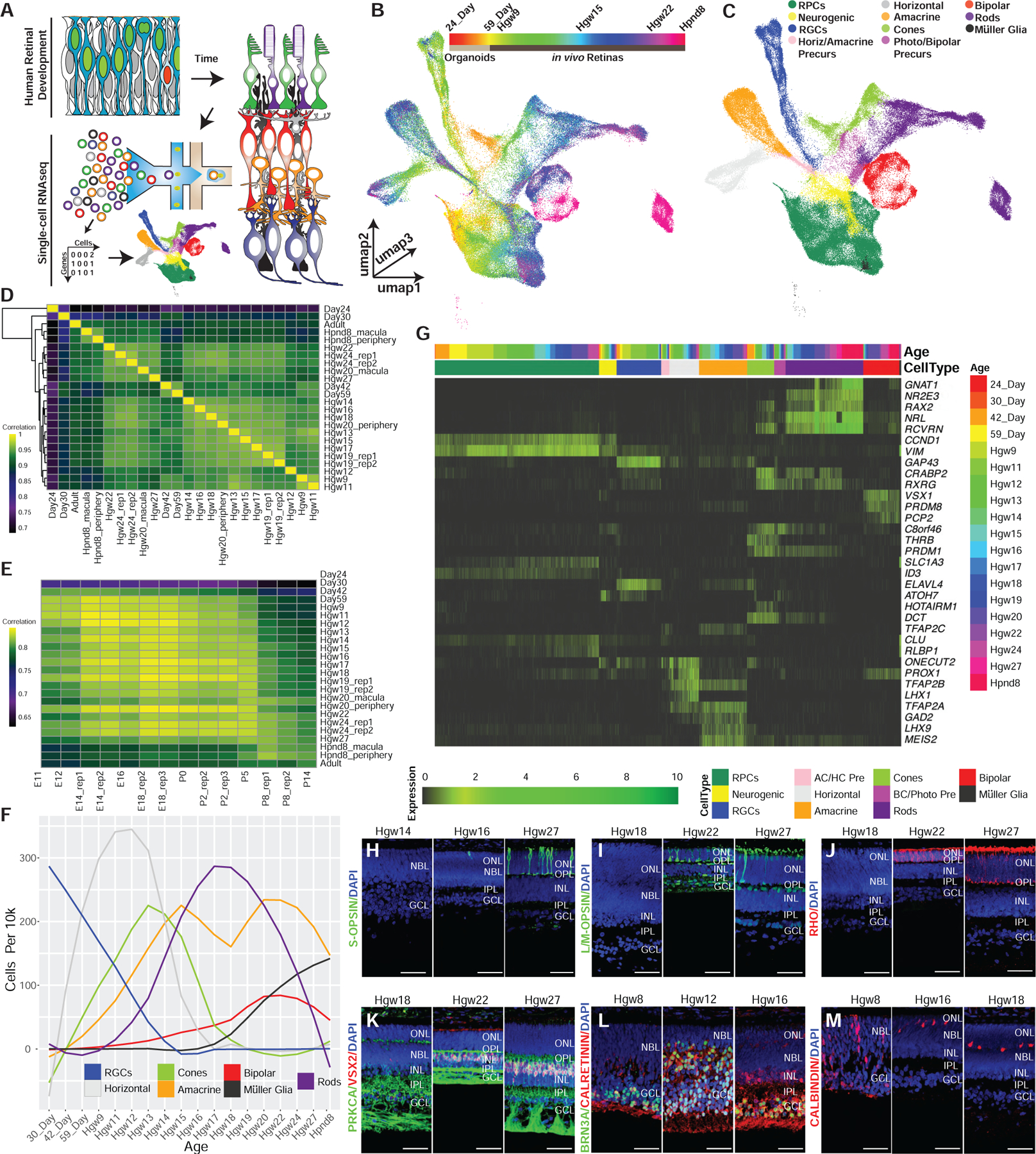
(A) Schematic of experimental design.
(B and C) 3D UMAP embedding of the retina dataset, with individual cells colored by (B) age and (C) annotated cell types.
(D and E) Spearman correlation between the transcriptomes of (D) human samples, or (E) across human and mouse retinal samples.
(F) Normalized specification windows of retinal cell types.
(G) Heatmap showing relative expression of transcripts with high specificity to individual cell types, ordered by cell type and developmental age (top annotation bars).
(H–M) Immunohistochemistry on primary human retinal tissue validating the dynamic expression of cell-type markers, including (H) S-OPSIN (short wavelength cones); (I) L/M-OPSIN (long/medium wavelength cones); (J) Rho (rods); (K) PRKCA and VSX2 (bipolar cells); (L) BRN3A (RGCs) and calretinin (horizontal, amacrine, and RGC cells.); and (M) calbindin (Horizontal cells). Nuclei are counterstained with DAPI. Scale bar, 50 mm. Abbreviations: Hgw, human gestational weeks; Hpnd, human postnatal day; RPCs, retinal progenitor cells; RGCs, retinal ganglion cells; AC/HC Pre, amacrine cell-horizontal cell precursors; BC/Photo Pre, bipolar cell-photoreceptor cell precursors; NBL, neuroblast layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer.
