Table 1.
Natural Medicinal Compounds: Their Active Constituents and Roles in Bone Health
| Sources | Chemical structure | Active constituent | Role in bone health | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 Turmeric |
 |
Curcumin | Works by modulating osteosarcoma, osteoblast, and osteoclast cellular function and thereby controls bone tumor formation, bone resorption, and new bone formation | [15–17] |
 Garlic |
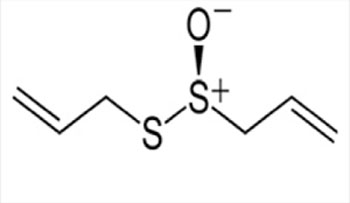 |
Allicin | Works by modulating osteoblast and osteoclast cellular function and exhibits its activity against bone resorption and oxidative stress-induced damage to bone | [18–20] |
 Aloe vera |
 |
Acemannan | Works by modulating osteoblast and osteoclast cellular function and therefore controls bone formation and resorption | [11–14] |
 Ginger |
 |
Gingerol | Works by modulating osteoblast and osteosarcoma and therefore controls bone formation and bone tumor growth | [21,22] |
 Soy |
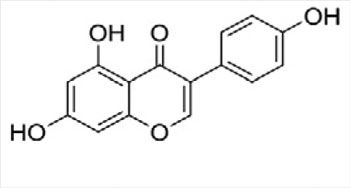 |
Isoflavones | Works by modulating osteoblast and osteosarcoma cellular function and thereby controls bone formation and chemoprevention | [28–31] |
 Green tea |
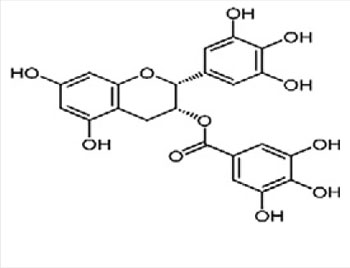 |
Epigallocatechin-gallate (EGCG) | Works by modulating osteoblast and osteoclast cellular function and thereby controls bone formation and resorption | [23–27] |
