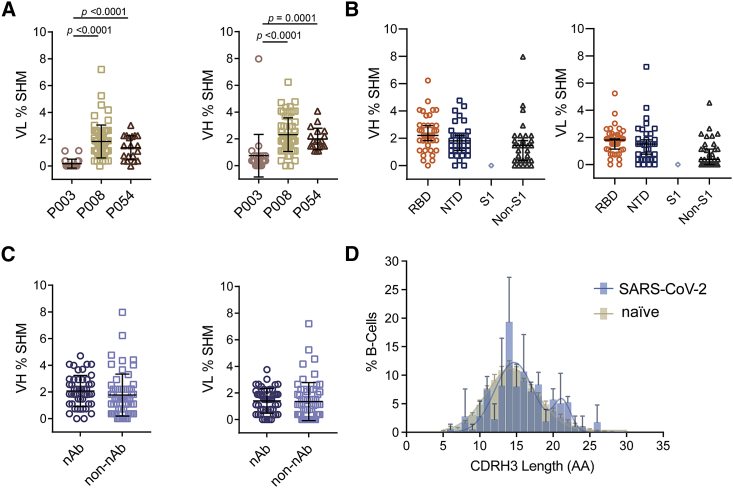
Figure 3.
Sequence analysis of SARS-CoV-2 Spike specific mAbs shows diverse gene usage and low percentage somatic hypermutation
(A) Percentage SHM in the VH and VL genes of Spike-reactive mAbs for donors P003, P008, and P054. Differences between groups were determined using Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparison test and p values <0.05 are shown. Black lines represent the mean SHM and error bars represent the standard deviation.
(B) Percentage SHM for mAbs targeting RBD, NTD, S1, or non-S1 epitopes (Kruskal-Wallis multiple comparison test). Black lines represent the mean SHM and error bars represent the standard deviation.
(C) Percentage of VH and VL SHM for nAbs and non-nAbs (Mann-Whitney 2-sided U-test). Black lines represent the mean SHM and error bars represent the standard deviation.
(D) Distribution of CDRH3 lengths for SARS-CoV-2 specific mAbs and representative naive B cell repertoire (Briney et al., 2019). Error bars represent the standard deviation between donors used in the analysis (n = 3 for SARS-CoV-2 and n = 10 for naive repertoire). A bimodal distribution of CDRH3 length is observed for SARS-CoV-2 Spike reactive mAbs. Also see Figure S2.