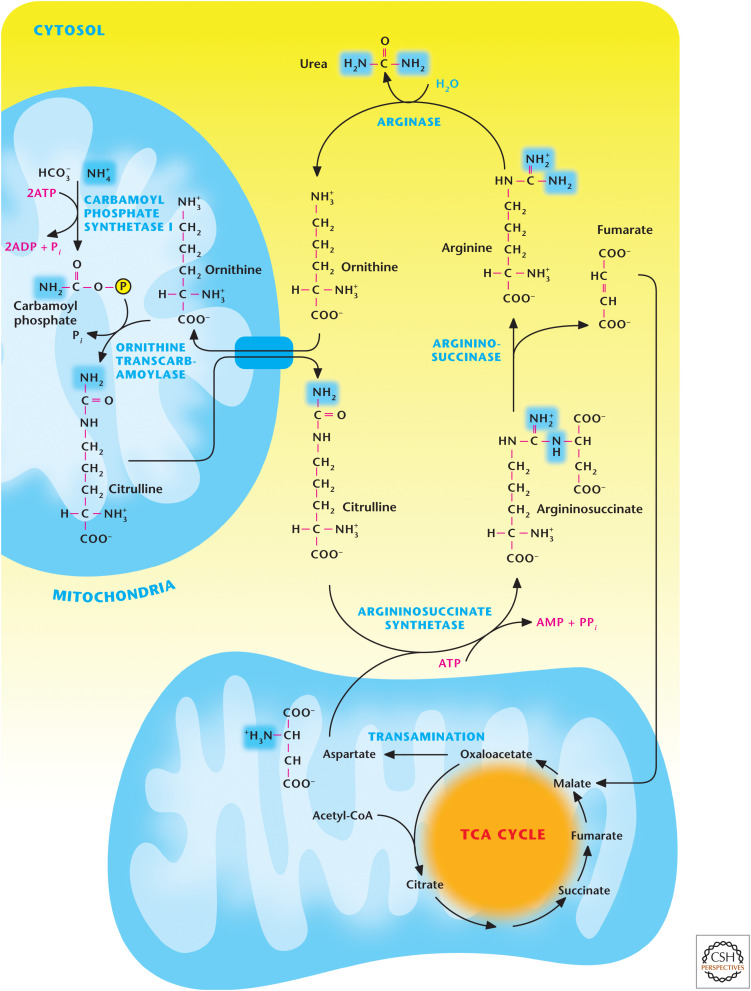
Figure 7.
Overview of the urea cycle. The initial step for urea synthesis is catalyzed by the mitochondrial matrix enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I to incorporate the first nitrogen molecule. Subsequently, ornithine transcarbamoylase uses carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine as substrates to generate citrulline in the mitochondrial matrix. Next, citrulline is exported to the cytosol and converted into argininosuccinate by argininosuccinate synthetase. This reaction results in the incorporation of a second nitrogen atom from aspartate. Next, the enzyme argininosuccinase cleaves argininosuccinate to produce fumarate and arginine. Finally, the enzyme arginase converts arginine to urea and ornithine to complete the urea cycle.