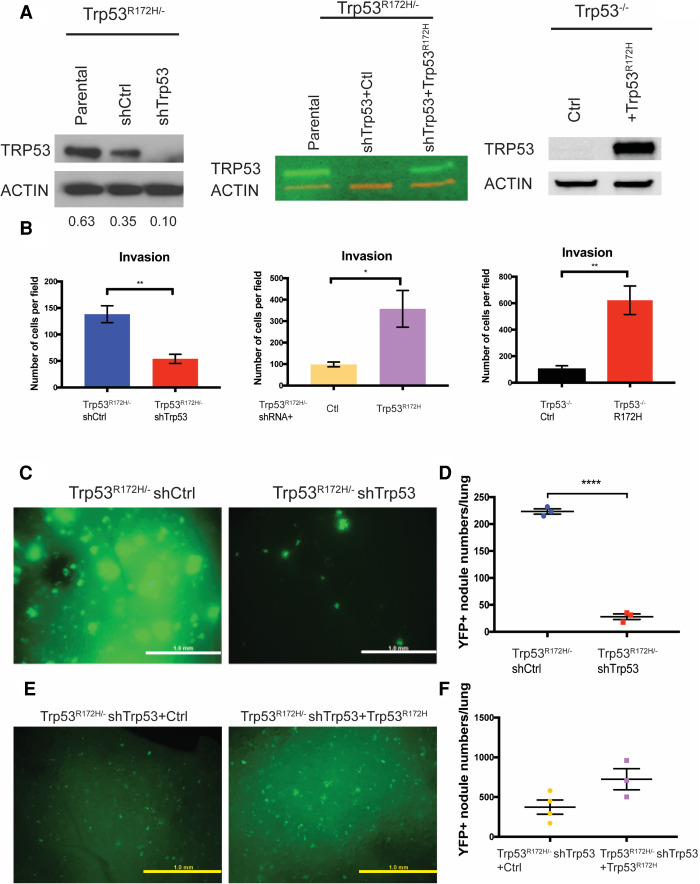
Figure 1.
Mutant p53 promotes ESCC invasion and lung metastasis. (A, left) Trp53R172H is depleted by shRNA in Trp53R172H/− cells. shRNA-resistant Trp53R172H is reintroduced to Trp53R172H/− shTrp53 (middle), and Trp53R172H is ectopically expressed in Trp53−/− cells (right). Relative intensity densitometry of TRP53 results are shown at the bottom. (B) Depletion of Trp53R172H suppresses cell invasion, whereas reintroduction of shRNA-resistant Trp53R172H or ectopic expression of Trp53R172H promotes cell invasion in a Boyden chamber assay. Trp53R172H/− shCtrl versus shTrp53, n = 4 per group, P = 0.0035, unpaired t-test; Trp53R172H/− shRNA + Ctl versus + Trp53R172H, n = 3 per group, P = 0.0398, unpaired t-test; Trp53−/− Ctrl versus R172H, n = 3 per group, P = 0.0094, unpaired t-test. Error bars represent SEM. (C,D) YFP+ ESCC cells were injected into the tail vein to induce lung metastatic nodules. Mice were sacrificed 8 wk after injection. Lung metastasis colony number in Trp53R172H/− shCtrl injected mice was increased greatly compared with shTrp53 injected mice. Trp53R172H/− shCtrl versus shTrp53, n = 3 per group, P < 0.0001, unpaired t-test. Scale bar, 1 mm. (E,F) YFP+ Trp53R172H/− shTrp53 cells reintroduced with shRNA-resistant Trp53R172H were used to repeat the tail-vein injection assay. Mice were sacrificed 8 wk after injection. Trp53R172H/− shTrp53-rescued cell line-injected mice had a trend of increased lung metastatic colony number. Trp53R172H/− shTrp53+Ctrl (n = 4 per group) versus shTrp53+ Trp53R172H (n = 3 per group), P = 0.0709, unpaired t-test. Scale bar, 1 mm.