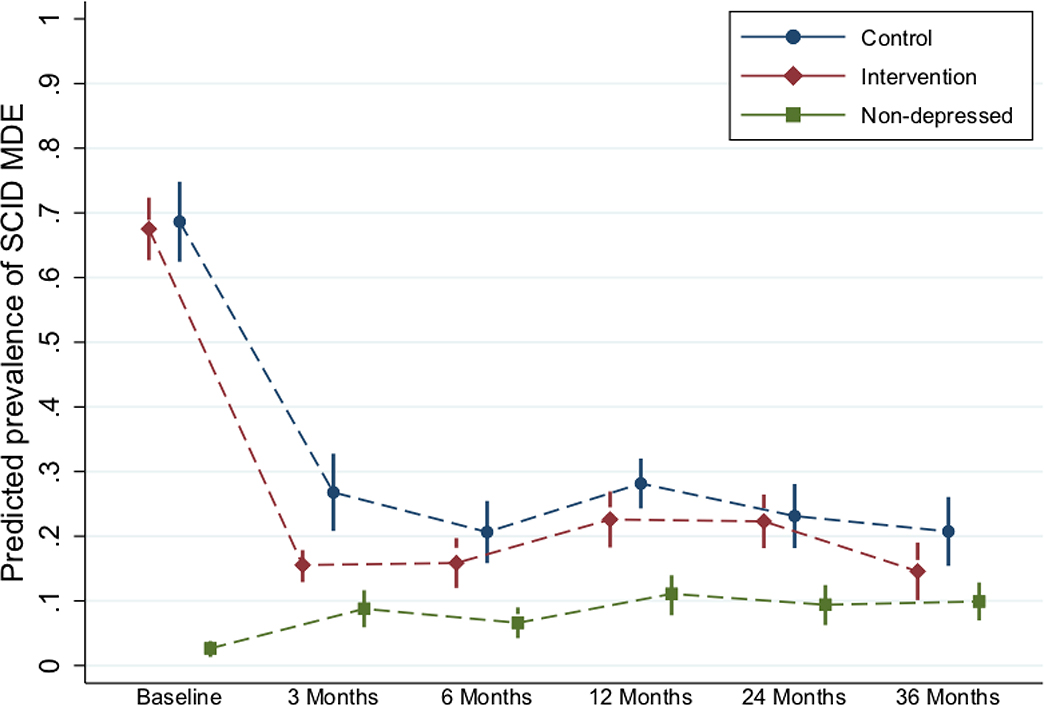
Figure 2: Depressive episodes (recurrence) across time points and comparison groups.
Note: *Abbreviations: SCID – Structured Clinical Interview for Depression; MDE – Major Depressive Episode.
**Predicted prevalences come from a longitudinal GEE model with SCID at all time points as the outcome. Time point, intervention arm (depressed in intervention, depressed in control, and non-depressed), and the interaction between these two variables are included in the model. In addition, the model is adjusted for the variables imbalanced at baseline or differential by missingness at any time point (see footnote to Table 3). An exchangeable working correlation matrix is used to take into account clustering by village cluster. Marginal predicted prevalences are computed from this model—at the average of continuous adjustors and the population percentages of categorical adjustors—and these are graphed by intervention arm.