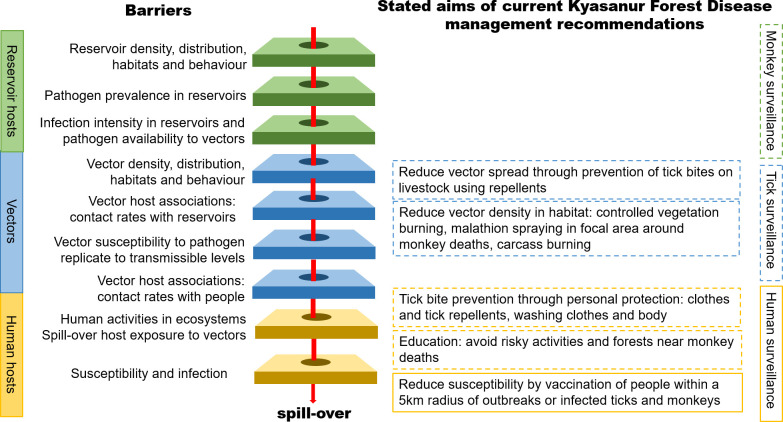
Fig 1. A schematic of the hierarchical barriers to spillover of vector-borne zoonotic diseases to humans, extending the framework set out in [10,14].
Management interventions may reduce or prevent spillover by targeting these barriers, with green layers representing reservoir hosts, blue representing the environment and vectors, and yellow the spillover hosts. Current KFD management shown on the right-hand side mainly targets the final 2 barriers associated with the spillover hosts, aiming to reduce human exposure and susceptibility to infection. The dotted outlines of boxes indicate where the empirical evidence for impacts of management interventions is particularly incomplete. Surveillance activity, currently conducted for KFDV in people, ticks, and monkeys informs these interventions, with dotted outlines indicating where strategies could be refined to better target interventions. KFD, Kyasanur Forest Disease; KFDV, Kyasanur Forest Disease Virus.