Fig 1. Scanning electron microscopy and fluorescent microscopy of C. sativa trichomes.
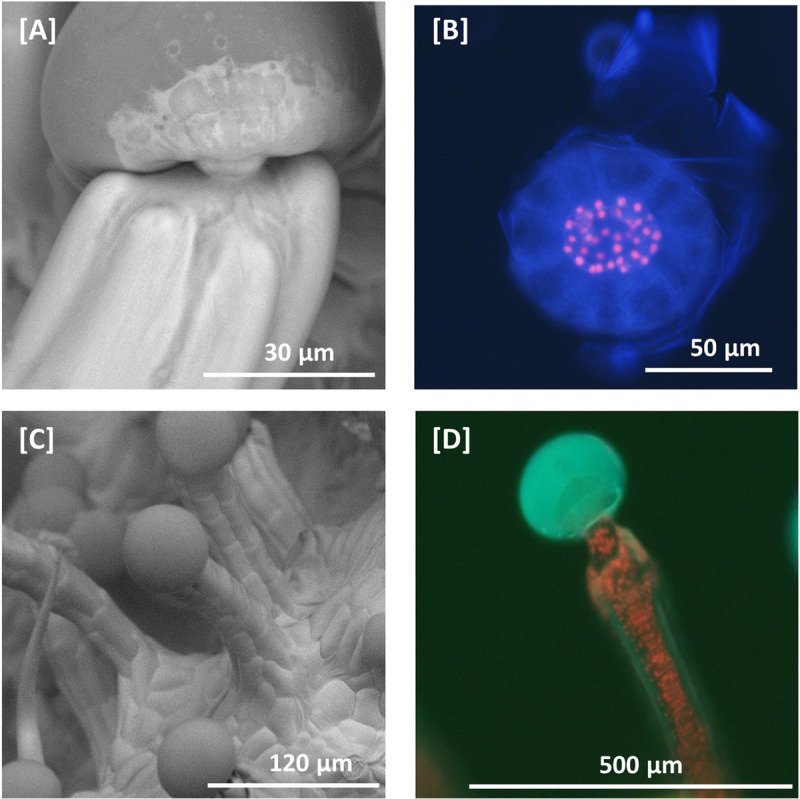
[A] SEM micrograph of a capitate stalked glandular trichome. Glandular trichome heads are morphologically distinct from the associated multicellular stalk. Glandular trichome heads are attached to multi-cellular stalks by a narrow constriction of the stalk. [B] Fluorescent microscopy image of a glandular trichome head showing the stipe cells (red fluorescence) that subtend the discoid layer of disc cells (no red fluorescence) at 400–440 nm excitation. Remnants of the ruptured cuticular layer covering the glandular cavity are also visible. Chlorophyll autofluorescence in red. [C] SEM micrograph of capitate stalked glandular trichomes, showing apparent continuity between epidermal layer and stalk. [D] Fluorescent microscopy image of capitate stalked glandular trichome at 400–440 nm excitation with gland intact. Secondary metabolites in the glandular trichome head fluoresce blue when excited, while chlorophyll in chloroplasts in the stalk fluoresce red.
