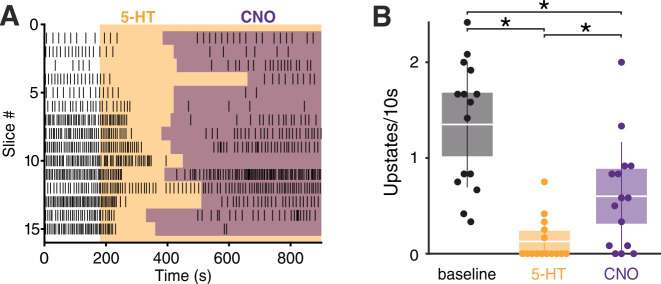
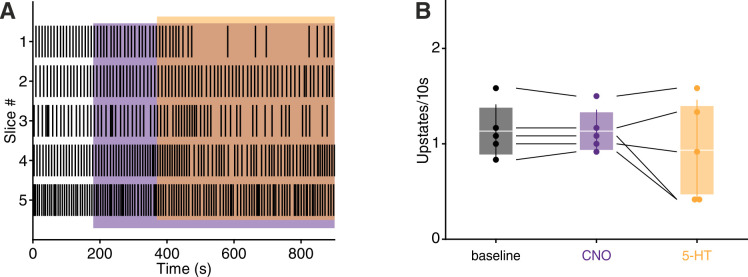
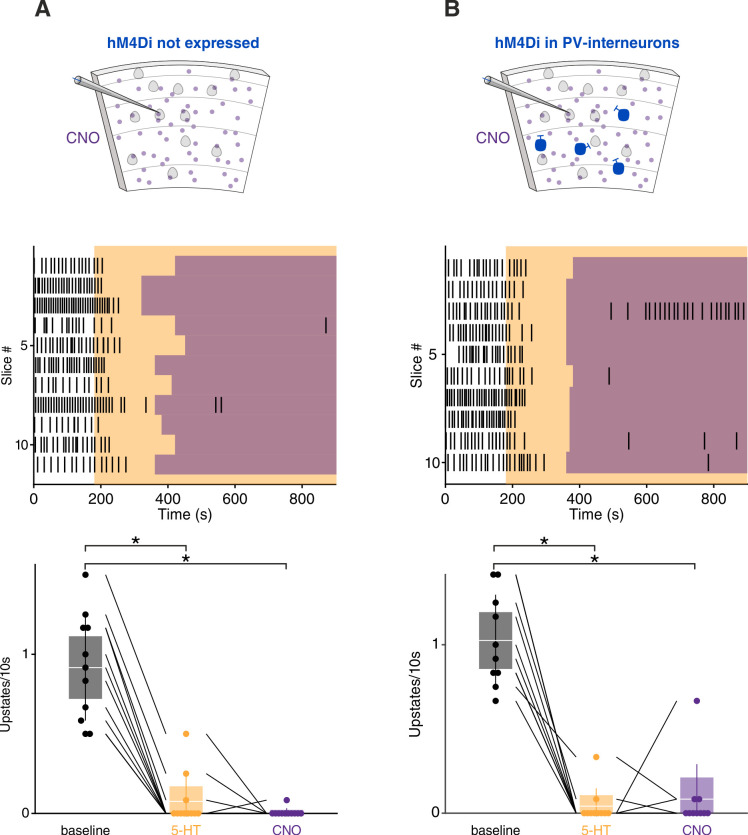
Figure 5. Sst interneurons mediate the effect of 5-HT on SOs.
( A) Upstate raster plot during 5-HT and subsequent CNO application. Orange box represents 5-HT, purple boxes represent CNO. Note the appearance of upstates after CNO application. (B) Upstate incidence during 5-HT and 5-HT+CNO application (n = 15; p (baseline vs 5-HT)<10–4, p (baseline vs CNO)=0.0482, p5-HT vs CNO = 0.0405, Kruskal-Wallis test). Patches represent 95% confidence intervals, lines represent standard deviation.