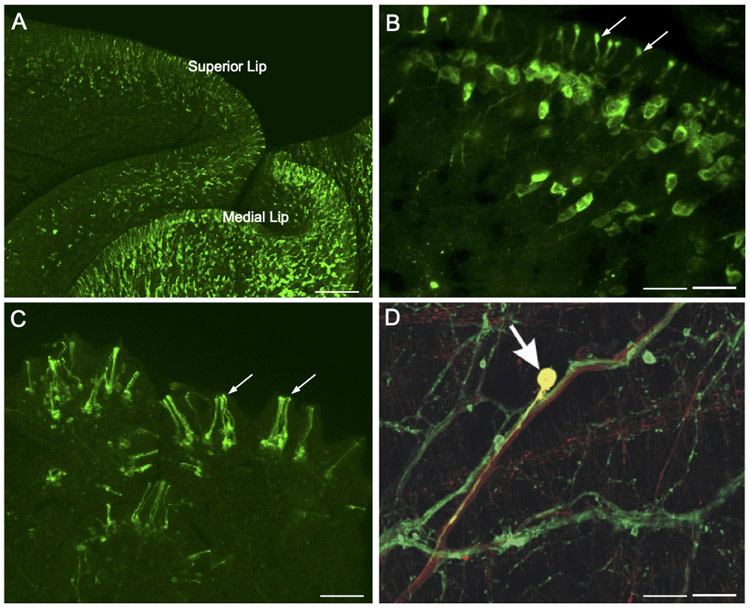
Figure 2.
Dopamine as a sensory neurotransmitter in gastropods. (A) Low magnification image shows abundant TH-like immunoreactive innervation of the lips in Biomphalaria glabrata. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) Higher magnification of THli cells in the mantle integument of Biomphalaria alexandrina. A single process from each cell projects through the epithelium, terminating as a bulbous enlargement at the surface (arrows). Scale bar = 20 μm. A, B: Reprinted with permission from Vallejo et al., J. Comp. Neurol. 522: 2532-2552, 2014. (C) THli cells in the oral veil of Pleurobranchaea californica. Groups of cilia-like terminations (arrows) penetrate the epithelial surface. Scale bar = 20 μm. Reprinted with permission from Brown et al., PLoS ONE 13: e0208891, 2018. (D) Esophageal nerve tracing (biocytin, red) and THli (green) on the surface of the pharynx of Aplysia californica. One double-labeled cell (yellow, arrow) in this merged image is a THli neuron that projects toward the CNS via the esophageal nerve. Scale bar = 50 μm. Reprinted with permission from Martínez-Rubio et al., J. Comp. Neurol. 514: 329-342, 2009.