Figure 4.
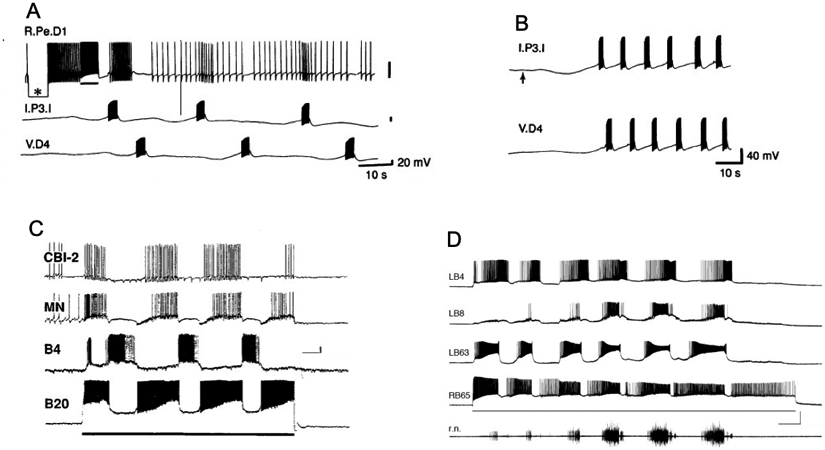
Dopamine activates central pattern generator circuits of gastropods. (A) The dopaminergic RPeD1 interneuron of Lymnaea stagnalis was co-cultured with interneurons Ip3I and VD4 for 24 h, allowing the three cells to extend neurites and form synapses. Passing hyperpolarizing current into RPeD1 (asterisk) established that there was no electrical coupling between the cells. Passing depolarizing current that caused RPeD1 to fire (bar below upper recording) initiated repetitive expression of the respiratory CPG rhythm. Reprinted with permission from Syed et al., Science 1990; 250: 282-285. (B) Two non-dopaminergic interneurons that belong to the respiratory CPG, Ip3I and VD4, were co-cultured for four days, allowing synapses to form between them. Pulsed application of DA (1 s pulses at 0.3 Hz, beginning at upward arrow) from a fire-polished micropipette produced alternating bursts of impulses in the two interneurons. Reprinted with permission from Syed et al., Science 250: 282-285. (C) Stimulation of dopaminergic neuron B20 produces rhythmic motor patterns in the buccal ganglion of Aplysia californica. Depolarizing current (line below B20 recording) was passed from an intracellular microelectrode. The buccal motor program was monitored in the buccal interneuron B4, an unidentified motor neuron (MN) in the ventral cluster of the buccal ganglion, and a cerebral-buccal interneuron (CBI-2). Calibration bars = 10 s, 10 mV. Reprinted with permission from Teyke et al., Brain Res. 1993; 630: 226-237. (D) Stimulation of dopaminergic neuron B65 produces rhythmic motor patterns in the buccal ganglion of Aplysia californica. Depolarizing current (3.3 nA, line below B65 recording). B65 fired in phase with the protraction phase neuron LB63, and out of phase with the retraction phase interneuron LB4. Activity in the radula closer motor neuron LB8 and on the radula nerve (r.n.) increased in successive cycles of the motor program. Calibration bars = 10 s, 40 mV, 100 μV). Reprinted with permission from Kabotyanski et al., J. Neurophysiol. 1998; 79: 605–621.
