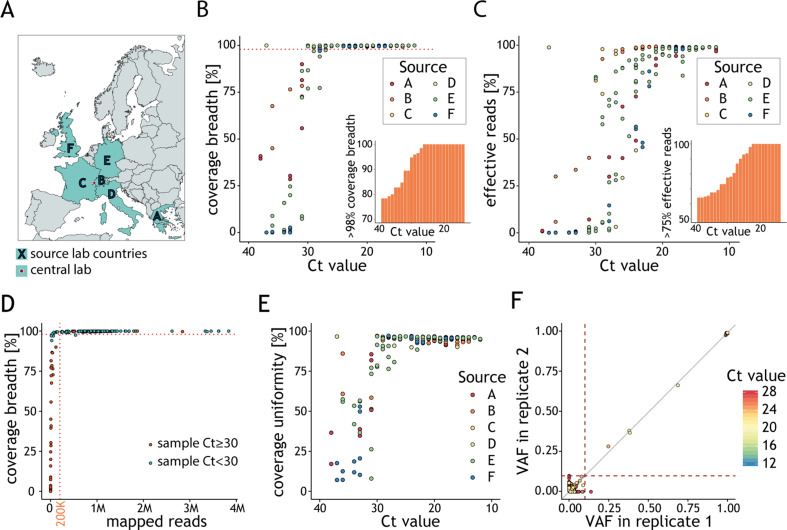
Fig. 4.
Viral genotype assignment in clinical samples reflects global genome diversity. (A) The multicentre study involved six laboratories, located in different European countries, which generated datasets analysed at a central location (SOPHiA GENETICS, Switzerland). (B) Fraction of viral genome covered by at least ten reads (y-axis) as a function of the cycle threshold (Ct) value (y-axis). Each point represents the results for a sample, colour-coded according to the source lab. The dashed line indicates 98% coverage breadth. The percentage of samples with at least 98% genome coverage breadth (y-axis) below a given Ct (x-axis) is represented in the inset. (C) Fraction of effective reads mapping to the genome of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (y-axis) as a function of the Ct value of the clinical samples (x-axis). Each point represents the results for a sample colour-coded according to the source lab. The percentage of samples with at least 75% effective reads (y-axis) below a given Ct (x-axis) is represented in the inset. (D) Fraction of viral genome covered by at least ten reads (y-axis) as a function of the number of reads mapping to the SARS-CoV-2 genome (x-axis). Each point represents a sample and is colour-coded according to its Ct value. The horizontal dotted line indicates 98% coverage breadth and vertical dotted line indicates 200K mapped reads. (E) Percentage of genome coverage uniformity (y-axis) as a function of the sample Ct value (x-axis). Each point represents the results for a sample colour-coded according to the source lab. (F) Relationship between variant fraction for variant calls in clinical samples processed in replicates and with genome coverage breadth >98%. Dotted lines demarcate variant allele fraction (VAF) = 0.1. Variants are coloured based on the Ct value of the replicate.