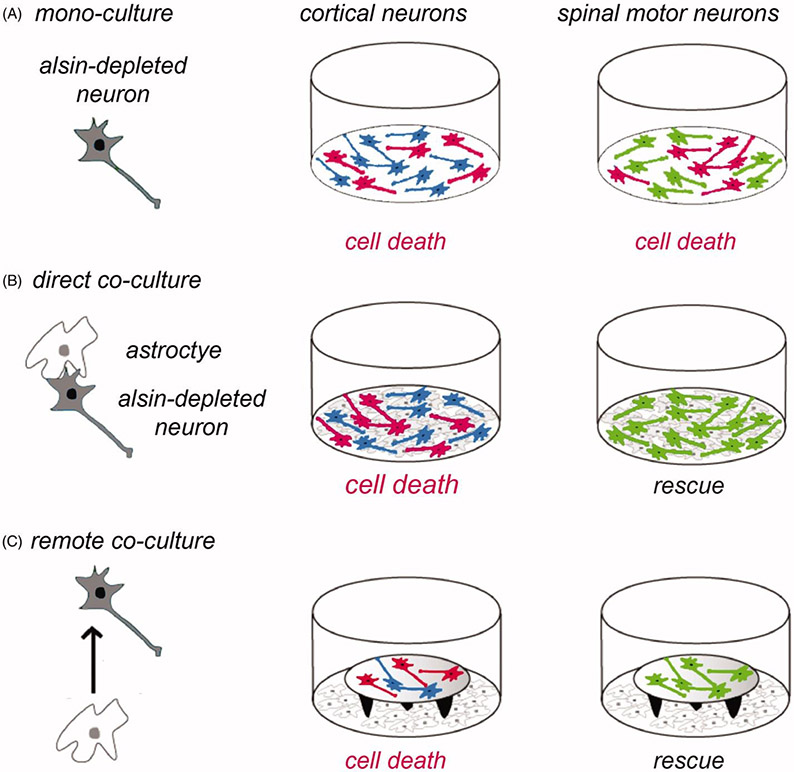
Figure 3.
Role of astrocytes in the vulnerability of cortical neurons to Alsin knockdown. The schematic shows the experimental design (left panel) using different types of neurons (in grey) in mono-culture or in co-culture with astrocytes (in white). Neurons having undergone cell death are depicted in red (middle and right panels). (A) Cortical neurons (in blue) and spinal motor neurons (in green) cultured each for 2 days in mono-culture show similar vulnerability to cell death (in red) induced by RNAi-mediated Alsin depletion. (B) In direct co-culture with astrocytes, Alsin-depleted cortical neurons display cell death whereas Alsin-depleted spinal motor neurons are completely rescued. (C) The astrocytic rescue of alsin-depleted spinal motor neurons (lower right panel) is mediated by a soluble factor as shown in co-cultures where the neurons are placed on coverslips on top of remote astrocytes. Neuronal viability was analyzed relative to control cultures transduced with a control small interfering RNA and using different types of astroctyes prepared from cerebral cortex or spinal cord (64).